HawkEye, also known as PredatorPain (Predator Pain), is a malware categorized as a keylogger, but over the years, it has adopted new functionalities that align it with the capabilities of other tools like stealers.
History of HawkEye
HawkEye emerged before 2010, with records of its use and sale dating back to 2008, making it quite long-lived. After several spearphishing campaigns in which this well-known malware was attached, it gained significant popularity starting in 2013.
This keylogger has been available on various dark web sites, even having dedicated websites where the tool was sold. However, this keylogger has been cracked for years and used by different actors without going through the subscription method imposed by its creators, whose price ranged between $20 and $50. This has contributed to its continued notoriety, and it has been used not only by criminal actors but also by script kiddies due to its ease of use.
Although it is not one of the most widely used malwares, it remains in active use and saw a significant resurgence during the COVID period. During this time, certain actors took advantage of the general hysteria to obtain company data through phishing campaigns.
Additionally, HawkEye has been used in conjunction with other loaders and/or malware that invoked this keylogger. Over its long trajectory, various actors and malware have been involved in attacks on companies, some of which include Galleon Gold, Mikroceen, iSPY crypter related with Gold Skyline, Remcos used on campaigns with HawkEye, Pony used on campaigns with HawkEye, etc.
Analysis in the ANY.RUN Sandbox
To conduct a quick analysis of HawkEye to extract critical data fast, we can use ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox. The service lets us easily upload and detonate a sample in a safe virtual environment and engage with it and the system just like on a standard computer.
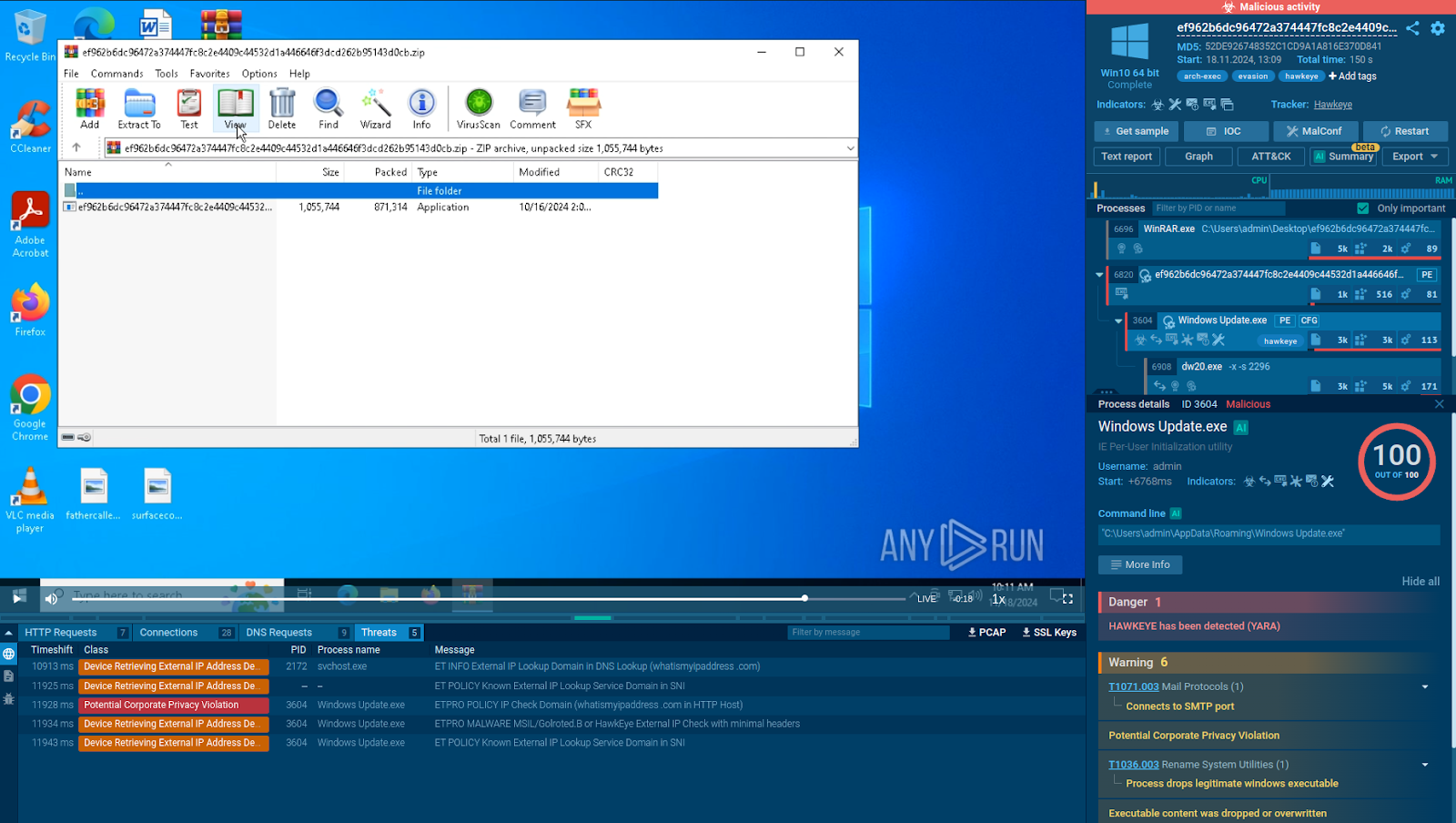
Analysis of a HawkEye sample in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Consider this analysis session, After executing the malware, the sandbox instantly identifies it as HawkEye and starts tracking its system and network activities. It also lists all the malicious actions performed by the threat and automatically maps them to MITRE ATT&CK TTPs.
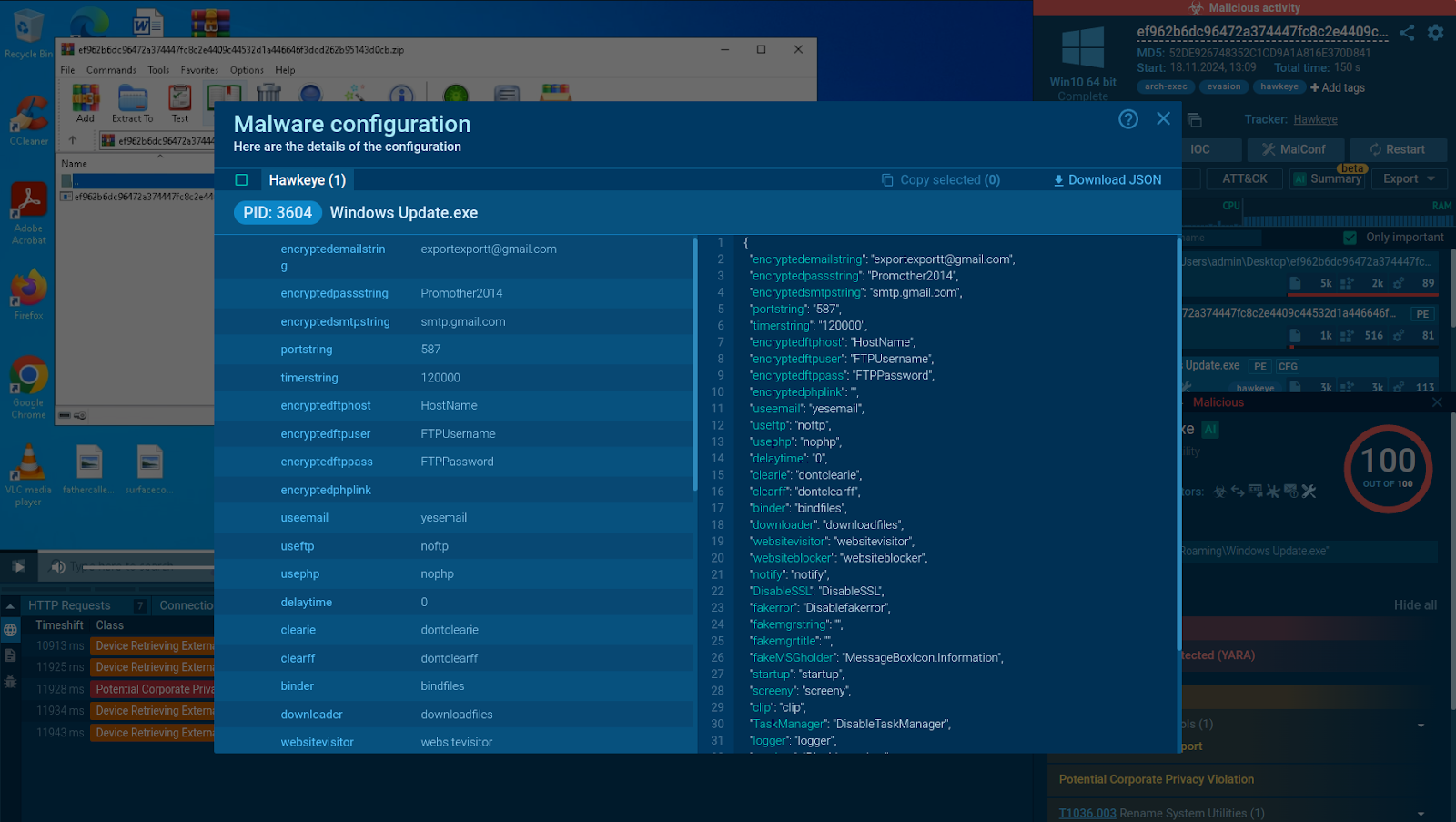
HawkEye config extracted by the ANY.RUN Sandbox
It also generates a comprehensive report, lists indicators of compromise (IOCs), and extracts the sample’s config information.
To start using ANY.RUN, request a 14-day free trial and access all features. You can also take advantage of a Black Friday offer to buy a license and receive another for free.
Technical Analysis
HawkEye’s delivery methods are quite diverse compared to other malware. However, its execution and behavior have remained relatively consistent over the years. A behavior graph of what has been observed in recent months would look as follows:
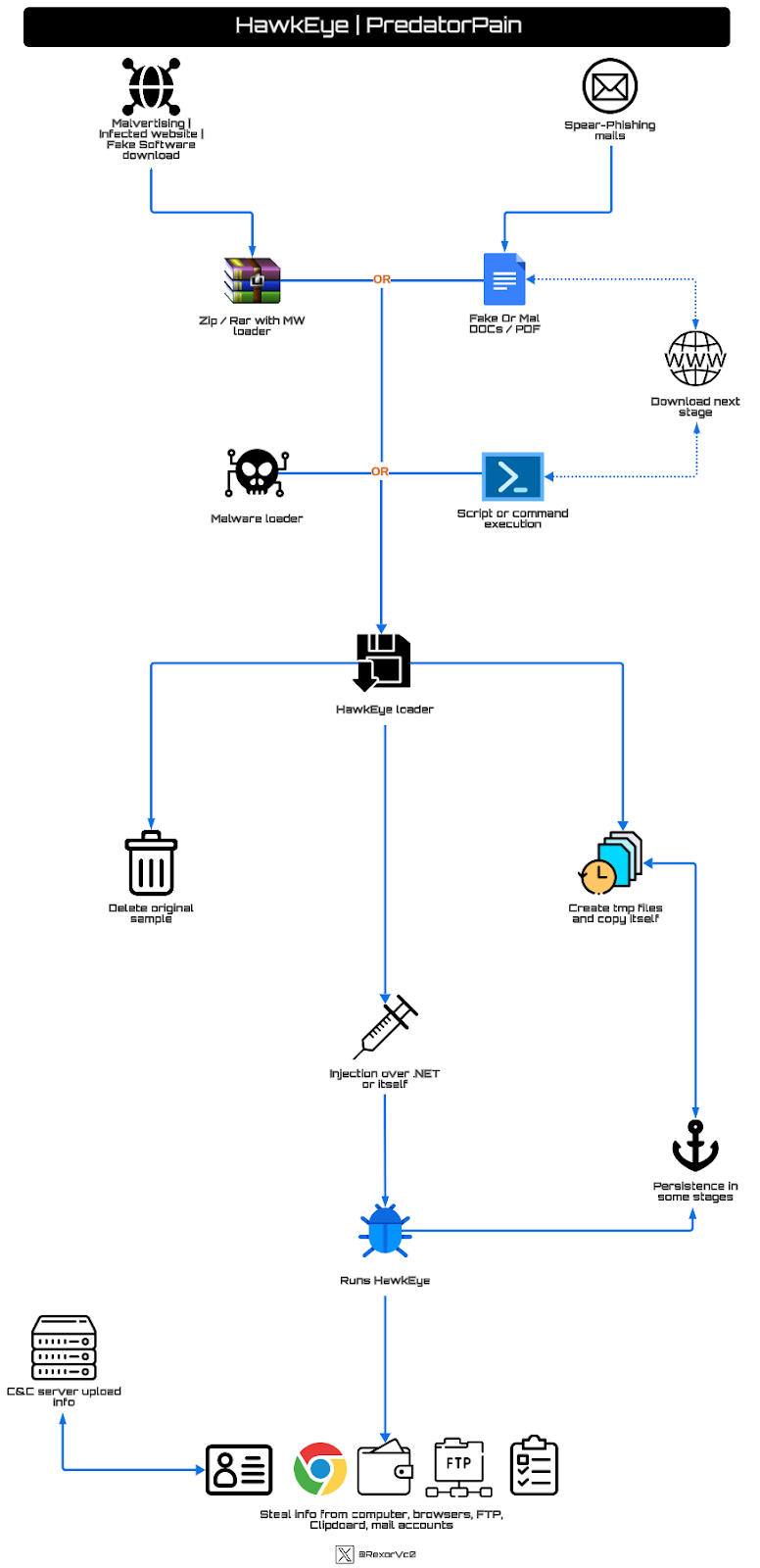
HawkEye graph
During the analysis process, I typically spend weeks, even months, collecting samples to understand how they function as a whole based on the existing variants. Therefore, we may observe variations among those presented. In most executions, we encounter enormous trees of processes based on their activities. To simplify, as you’ve seen in the previous graph, it’s not as complex compared to other stealers or RATs. It generally consists of an executable that drops others in temporary paths, then injects code into one of them or into a .NET-related software. Later, in memory, it gathers all possible data and sends it to a C&C.
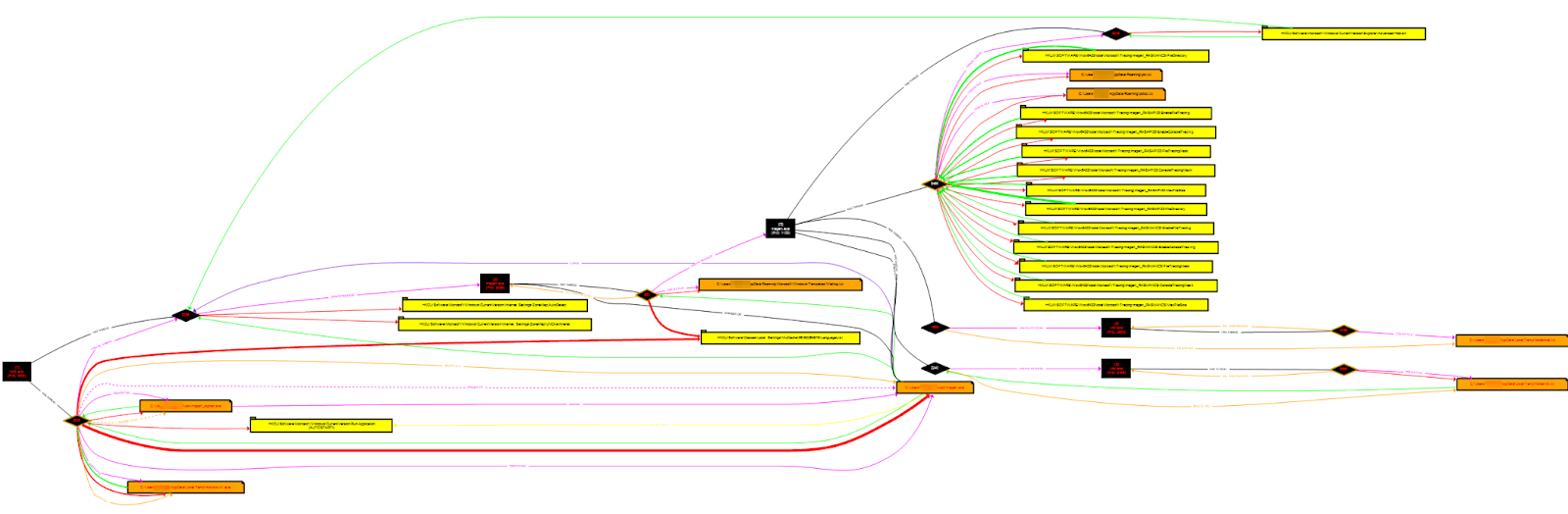
ProcDOT detonation chart
Going straight to the point, in an initial execution of one of the samples I analyzed, we see a rather extensive process—a succession of execution copies launched in temporary paths.
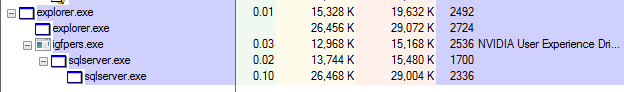
Process Tree execution (Image 1)
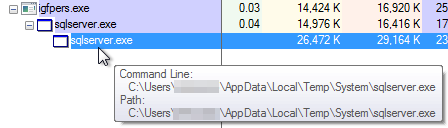
Process Tree execution (Image 2)
In this instance, they used the RoamingTemplates path, but this is highly variable depending on who created it. Generally speaking, they tend to abuse paths like AppDataRoaming and AppDataTemp, which are classic choices.
Paths commonly abused (Image 1)
![Зехр]огег ехе igfpewexe igfpewexe 2492 2536 2536 С [ JseB 03t в Тетр Syst ет vigfpeB ехе Ster1 Theed](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXfq_1RXyGRnK2p2SykXDW_pnnsUHhZEMxrzva1cWfDeDl_N4VoimWXQgmjyKFDOa2fKsfoWzAuaKZULGYegKJvAnEEhYvcPSqGRAPonvikoJjJXC86LxBYSqWv9RuSfVwEc2MC4ONL0ZOzu6jWJNC8?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Paths commonly abused (Image 2)
Paths commonly abused (Image 3)
Here’s the list of paths observed for dropping files:
- C:Users<user>AppDataLocalTemp
- C:Users<user>AppDataRoaming
- C:Users<user>AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWindowsTemplates
- C:Users<user>AppDataLocalTempSystem
- C:Users<user>Music
All of these files that are launched, and which we’ve observed executing in the previous step, are copies of themselves. The filenames are also highly variable, as you might expect, but they often try to have an icon that makes the victim think it’s a legitimate program, or the malware description might be altered to make it seem like legitimate software.
Ultimately, after comparing the dropped files, we can see they are simple copies of the original, with the particularity that some versions launch them in hidden mode, so you can’t see them unless you’ve enabled the “View hidden files” function in Windows.
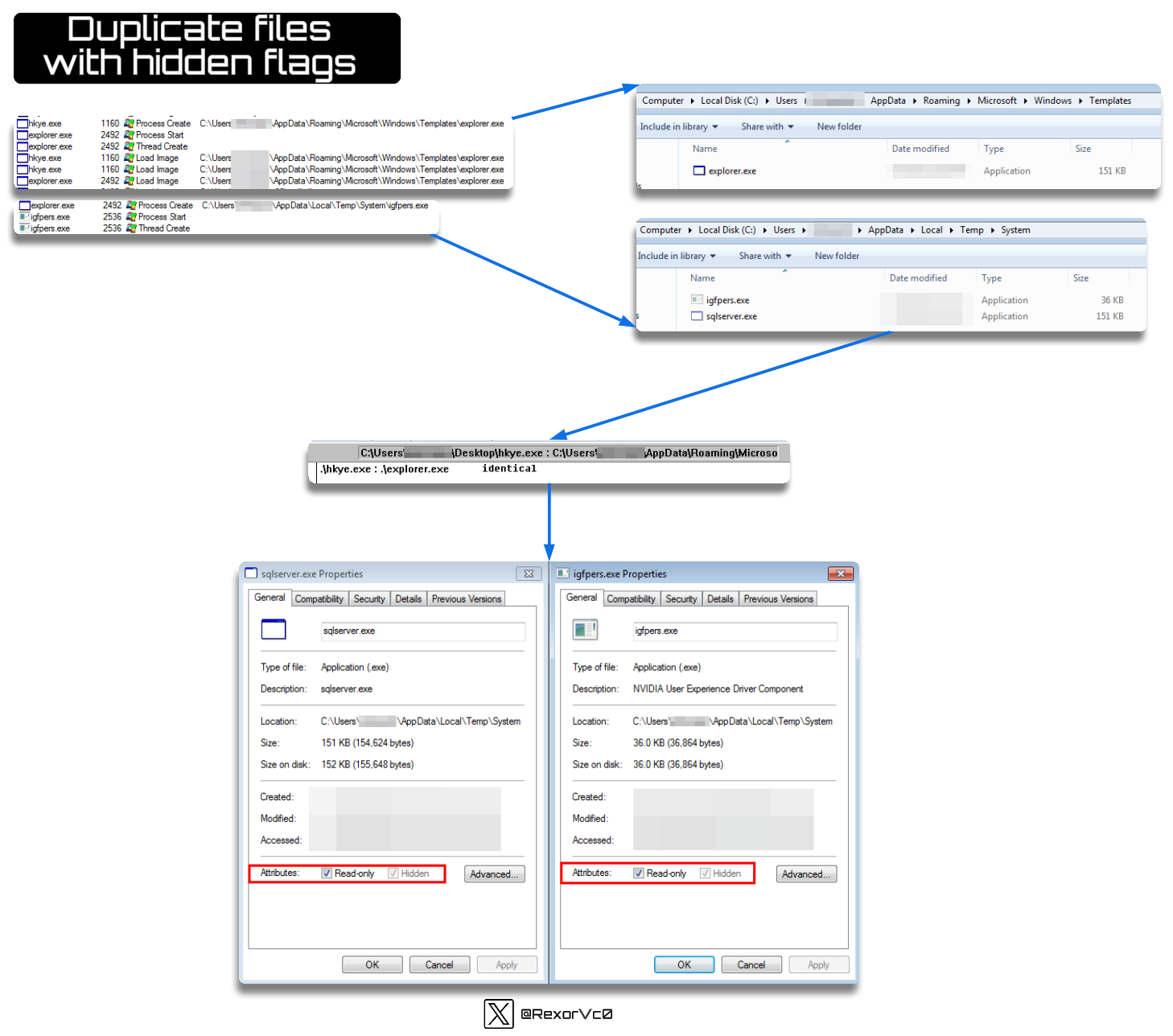
Hidden files duplication graph
During these file droppings, we can encounter both replicas of the original file in different paths, as well as support files whose functionality is typically to establish persistence (or check if it’s already done, and if not, do it) and to perform injector functions, which is a characteristic of this malware. In this case, the smaller binary is responsible for these actions.
Injector written in temporary folder
I check to see if there is any shared information between the two binaries and notice that certain parts of the code match the original. This will become relevant later, as right now we’re seeing them separately, but everything will make sense afterward.
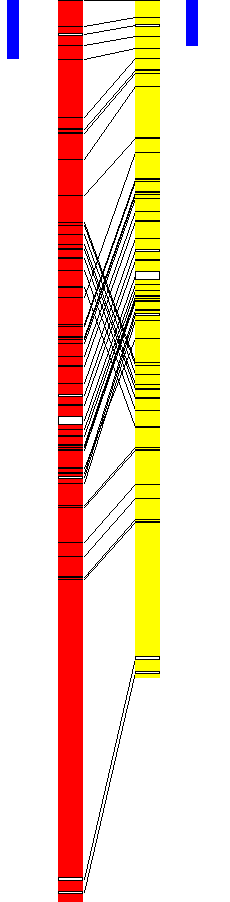
Comparison of the injector and the Hawkeye bin
After this step, we can see how persistence is established. PredatorPain isn’t just a malware that establishes persistence once—it’s been observed to check and establish persistence up to three different times, depending on the phases (Loader > Injector > Payload).
This makes it clear that the malware is determined to persist on the system, one way or another. At this stage, to avoid revealing persistence mechanisms through strings, it obfuscates a string and then decodes it to introduce, in this case, one of the binaries launched earlier. This practice isn’t as common and adds a level of sophistication not found in other samples.
![public string e(string —int e. Length; e 255; num2 = Persistence hkey e) array chart) array = e.ToCharArray(); while (--num e) (char) ( array [num) return string. Intern (new string(array)); registryKey Identity Name SubKeyCcunt ValueCcunt checkMode keyName rerncteKey _identity Static members e . a Cnum2) e)); 11) [21 [3] [5] [71 [8] OxEA8F true); Type REG_SZ array [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [7] [8] pubLIC static void ResistryKey registryKey if (resistryKey null) return; resistryKey . Close ( ) ; Resi stry. CurrentUser. char[Ox00000009] ox0073 's' ox006C 'l' 0*0073 Software CurrentVersion Run} Btringto—l] -NVIDIA User Experience Driver Component- {H KEV_C URREN T_tJSERlSoftwa tv ersion IRun ) rrentVersionRu n" Default Microsoft.Wi n32. SafeHa ndIe-s.SafeReg istryHa n d I e rrentVersionRu n" false Name valueNames (01 str array Opera bon; Result: Durabon; Type; Length: RegSe tVaIue HKCU Software Run WVIDIA user Experience Driver Component o, 0000233 NVIDIA user Experience Driver Component C p oca gfpers. exe c. •Xuses REG _SZ C: users @ NVIDIA user DnverCompone-t NVIDIA @RexorVcz exe KAppDa ta uocal ITempS ystem exe](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXf8gObBhWpZ4hHZ0LG78OstkYe6Zu3gEcGjxmKZC2_8TEK_GsFk-rCBI1537q_a_Q6UqENdxyMX9ft32rczhzp09t4lu2kYkU_0rPtXWOgjaKgiKcV4nlgHNzmMhL80TtlvvgeQ8C_4VVD3hBRj__M?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Hawkeye persistence in registers
Not only does it create persistence in the registry, but we also find samples that establish persistence in tasks using commands like the following:
schtasks.exe /Create /TN “<Path><TaskName>” /XML “<File>”
After observing its behavior in the early stages, we delve deeper into the entire execution thread throughout the analysis phase with debugging. I’ve followed several samples, and they’re mostly similar—samples in .NET, sometimes obfuscated with tools like Confuser, Eaz, Reactor, or similar, which are relatively easy to deobfuscate.
![public string u2FW, int num = u2Føø.Length; int num2 = u2Føø & 255; int u2Føø) chart) array = while (--num e) array C num) (char) —return // Token: axa4øøøøaA RID: la public static readonly Xu2Fß3. Xu2Føa Xu2Føø; // Token: axuøøøøaa RID: 11 private byte[] Xu2FßI; ((int)this. u2FøICnum2) u2Føø));](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXfwOLSggdAivS5KhF_yVYLNOCwr2fY7os5w7QCk0wDHvpJGafS8sYmWIiMT6fDmtCII-v184R9uMPR8hrYEkkl0Lw8EpbB6zsQcIYOJNr8d1KgPmhc0srRqPetzk1odwepOIbbIvCRM97czEjw47pc?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Hawkeye code obfuscated
In most samples, I noticed heavy interaction with resources, which will become crucial shortly since I observed a significant amount of data in these resources across most of the samples I found.

Resources data content (Image 1)
![ss 2€ ]соп ]соп Grou2 0000EFBz 0000EF>z 0000EFzz 0000EFEZ 0000Fooz 0000F02z 0000F04z 0000F0Ez 0000Fnz 0000Fozz 0000F0Ez 0000F10z 0000F12z 0000F14z од 24 21 42 91 Ез 23 92 64 67 24 43 22 92 64 67 25 53 Ез 22 зв 70 67 Ез вв 70 52 Ез 32 вв 70 Ез sc 32 вв 70 2€ 67 72 во вв 70 29 ss 67 35 33 вв 41 во дз 67 36 34 42 51 47 67 €2 34 42 52 70 24 29 зс 25 2€ yR@rZ ) з глллллллллллт 34 94 24 вв 23 27 вв 47 29 вв 21 52 33 вв 44 21 вз вв 53 20 вв 07 41 23 40 вв 24 дз вв 25 04 вв св 43 72 вв ЕЕ вв 42 29 вв 28 76 ЕВ сз Ез BVZSERIYUJGF+_) • ссссдддд±еее 3444тттт cddppppp ееееееееееее fggg XXXXL](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXcNakoiyob5fjQvQQKD8KLv4NxrLtgvWueZfLVDRLVdQzVMGF_qjiaAl85SJIVmeQx10JOpYAY_P0Jd9CaL7yYfsRiVPpn1FBO_G61qUzZgK0WT753XO3zvwZvXaE8kflC0Ici8-CHz1YRfbzKmJ_I?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Resources data content (Image 2)
In the malware’s initial phases, it looks for the running process (which will be the previously prepared copy), where it will check the PID to access the resources. Within these resources, we see two distinct types of code: the initial part, which acts as a key, and the data chunk, which is what will be deobfuscated. To achieve this, it uses XOR + Poly, and at the end of the process, it extracts a Portable Executable.
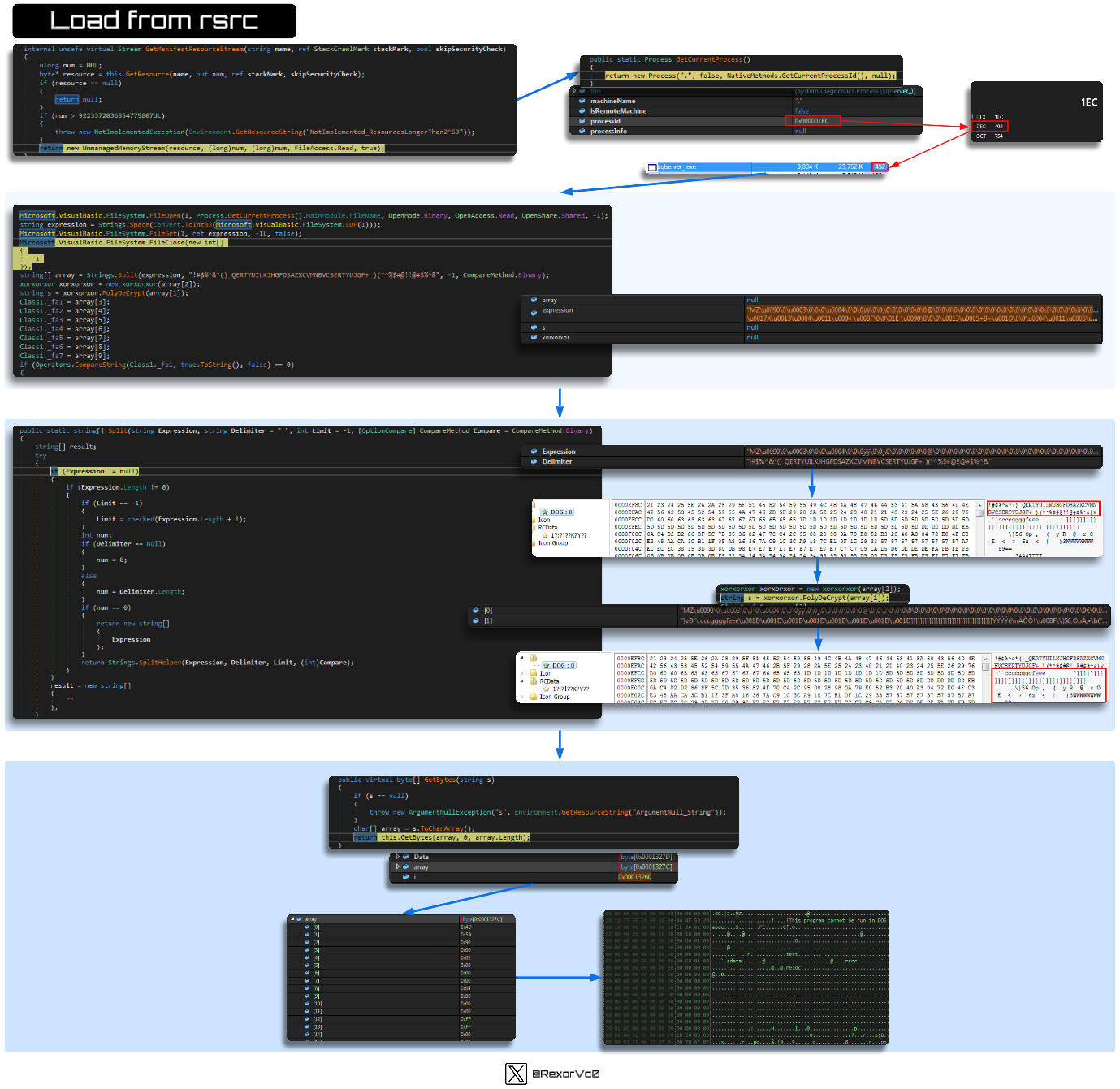
Graph of binary load from resources
It can do this in various ways depending on the sample, but we see the same extraction of a binary from a resource as we do from obfuscated code in memory, like the example shown below.
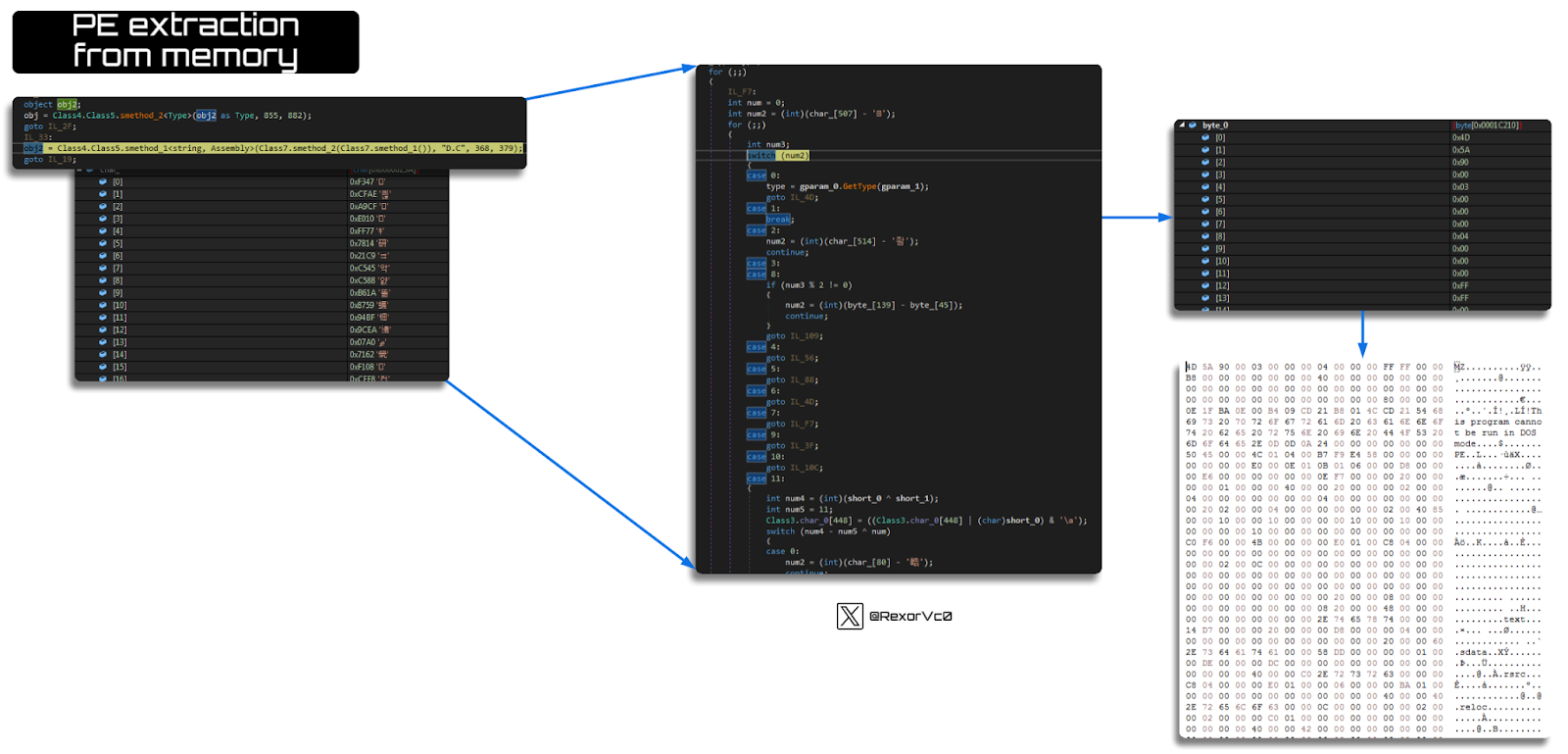
Graph of PE extraction from memory
The result of this phase is two extracted files—one will be the injector, and the other will be the Keylogger.
![File extract Entry Point : File Offset : Linker Info : tile Siié: 0000F5EE 0000D9EE 8.00 0001220% 00 EP Section : First Bytes : Subsystem : FF 2500 20 40 Windovvs GUI 00004209 32 bit- Library RES/OVL : O / 22 % MS Visual ce / aasic.NET VB 2005 -DLL -EPToken : 00000000 , overli Lamer Info - Help Hint nu•pack info aig sec. 01 , [I*EXE PE found], Warning : NETRES 36.22KE,tr](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXfWr9K4ilzpP1LlhJDMjBfnmHFfQuIt1L6jKmVRp2-7Usjhaw3A6vML3pL5zRWheVA1rUzoSIM2ATvrl2FtedfVxQxDu2jCX0xkGZiaF4torEwEkGtwPbHaUvli0E_688rnnhszhjl7VyI5UykIS-o?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Extracted Injector
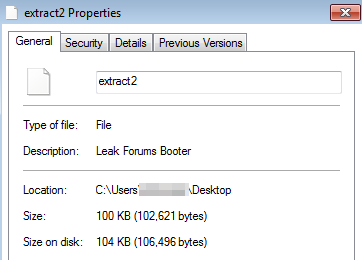
Extracted Keylogger
I compared both files, and they’re entirely different, in size, in structure—the only common factor is that both are .NET binaries.
Binary comparison
To highlight the difference between the injector dropped on disk (Right) and the one extracted from memory (Left), we can compare the extended content. We can observe how the memory-extracted injector includes imports related to injection that the disk version doesn’t (such as ZwUnmapViewOfSection, VirtualAllocEx, WriteProcessMemory, etc.).
Extracted and dropped injector comparison
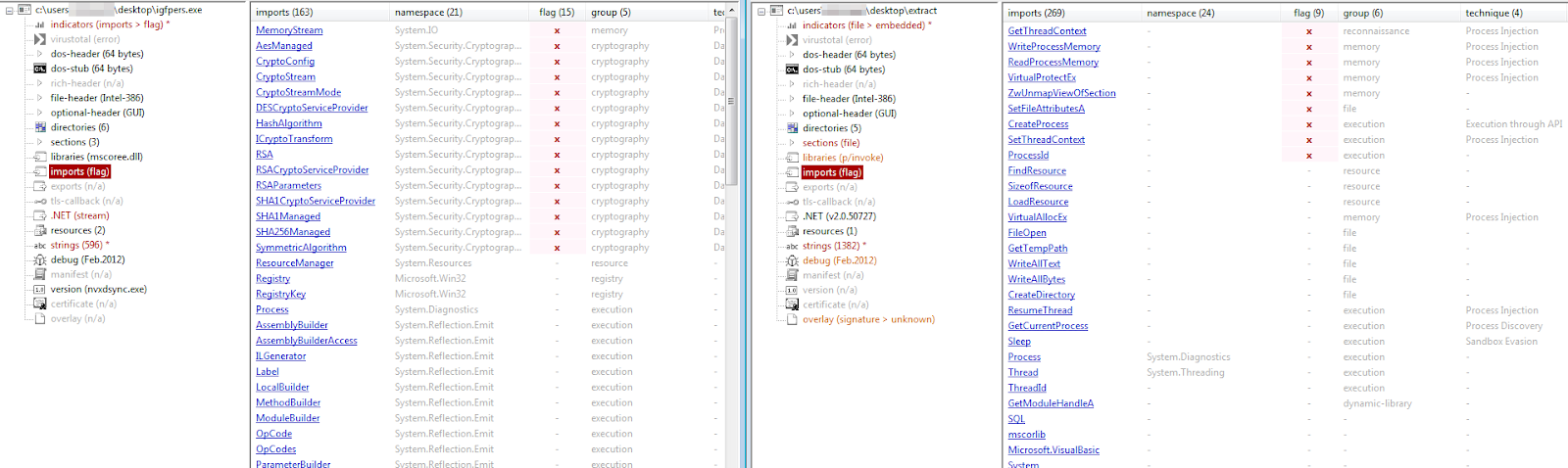
Extracted and dropped injector comparison
Here we can observe various functionalities while extracting the binaries, such as self-deletion. This is done to maintain evasion and avoid revealing its location, as it drops replicas of the original binary in various locations, as we saw earlier.
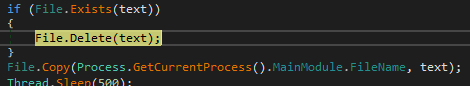
Self-deletion and self-copy of the original binary (Image 1)
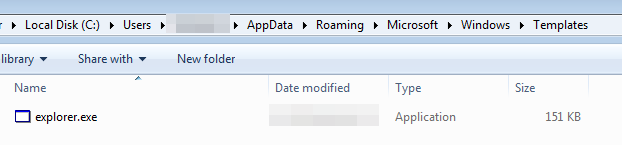
Self-deletion and self-copy of the original binary (Image 2)
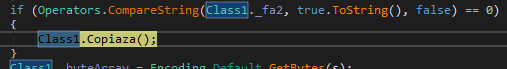
Self-deletion and self-copy of the original binary (Image 3)
![array expression (string[OxOOOOOOOA]](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXenqHvozxFTpudnB23VGk39QYFTA3LjAXY3sCya9vdwP-bKs4f4AiD4gK9CzvwSB8LWjVuSvVGfnLwbNkhrL9s41H-zrf31QNSXqePiqSxDrblLCXHgfiPM90Jq_P71Sv2LRPyjNM2Lk_f7cHN3D1c?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Self-deletion and self-copy of the original binary (Image 4)
One of the dropped files, the smaller one, acts as the injector. When extracted from memory, it has more functionalities than the one seen on disk. This is because the injection tasks are carried out during runtime, but the written file is actually a portion of this, triggering the main binary located in the temporary path.
It checks persistence and restarts the entire process, including injection. Therefore, it’s a part of the file without revealing all of its functionalities. I’ll show you how it performs injection using Process Hollowing.
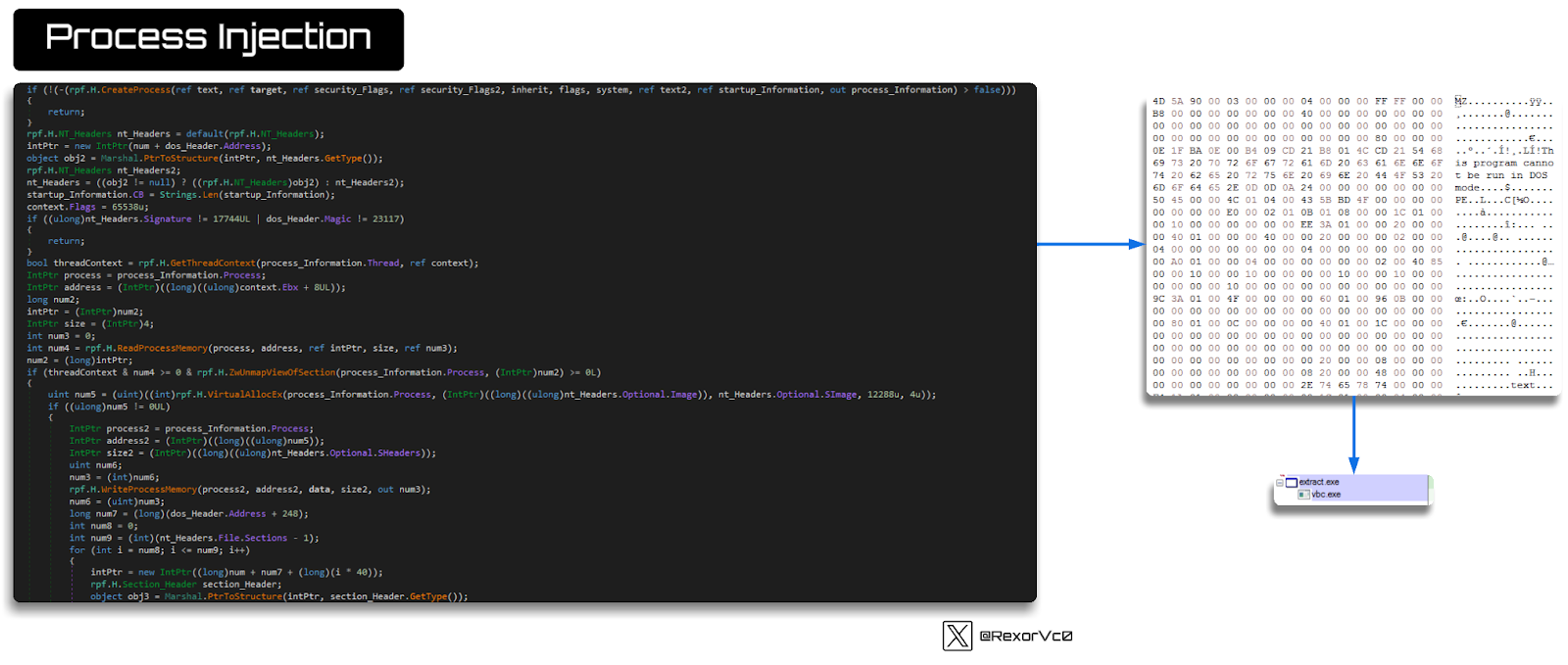
Graph of the process injection
In essence, the injector doesn’t have much more functionality. It includes a phase where it checks running processes, which is an interesting technique to detect analysis tools or to determine if the process is already running. If not, it launches the process, adds it to the registry (as seen earlier), and restarts the execution.
![public static roces GetPncesses (string machineName) bool flag = P n ager . Is Remotema chine (machineName) ; ProcessInfoC] processlnfos = : anage- . Getp-ccesslnfos (machineName) ; Process(] array = Process(prccesslnfcs. Length], for (int i = a; i < processlnfos. Processlnfo processlnfo = processInfosCi); array C i) new Process (machineName, flag, processlnfo. processld, return array; process Info) ;](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXe6WRElehR9lJjOhJxDoJSyQflv6icUDQW4VhFAxBWTEGtgKzY8PYRZu7SRatYeROmIGBMSoIzh2hnp-MKYmjtGCsGXPXWQrkbyDD0Hx0VZn87i1EE1kLG0om1DhedF2M6VW7DiyXqhJ5wEZCJogQ?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Process collection routine (Image 1)
![[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [24] [25] [26] System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System. Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo System.Diagnostics.P rocesslnfo](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXc8nRZgaYEpPFIyPcRI_xaJb8n49EtUHxAG4AI-liuCCW5jTgLqi8DfXE_sDOjLFRc0jWoco75lu_Dok6-KUuKsnT9m0i138MzF7nOHlirH8QF89n_cLPiNXjrDMvqWWlZASv9ul-PxL-XBNC-uxmw?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Process collection routine (Image 2)
![array [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] System. Diagnostics.P r ocessu0000032] {System Dia g nostics. Process (services)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (sqlserver)} {System.Diagnostlcs.Process (svchost)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (svchost)} {System Dia g nostics. Process (svchost)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (svchost)} {System.Diagnostlcs.Process (lgfpers)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (notepad)} {System Dia g nostics. Process (procdot)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (wmpnetwk)} {System.Diagnostlcs.Process (procexp64)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (smss)} {System Dia g nostics. Process (csrss)} {System.Diagnostics.Process (Ism)} {System.Diagnostlcs.Process (svchost)} {System Diagnostics. P rocess (V80xTray)}](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXe9KB11z6qfzTNxxx1WfI58i14sT57AfEyWem0Hr_j4QUSde01HPdEs2HoRfhn_KqM104N1RbJjM1Uvaa82mZjhWv7-nyYO-B3YbG4b8aYY5X_HjcWCKrsF0n4kMo8UkPcyYeLEKdKoK9DPAJdbHbc?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Process collection routine (Image 3)
Lastly, we only have the second extraction left to observe, which is HawkEye itself. I’ve encountered many versions of it, as the modules included will vary significantly based on what the creator configures in the builder of the Keylogger itself. We’ll talk more about this later, but you can see all the functionalities that can be added during its creation, which will impact the modules incorporated into it.

Comparison between crack and extracted keylogger features (Image 1)
Comparison between crack and extracted keylogger features (Image 2)
At this point, I conducted tests with several builders to verify this theory, as I had extracted multiple samples to the final phase, and almost none of them resembled each other too much. I tested by removing or adding options, and even with the same sample, there were significant differences, so you can imagine how different it can be if it’s not exactly the same version of the keylogger and different elements were selected during its creation.
Comparison between crack and extracted keylogger
At this stage, we just need to examine the payload’s functionalities. Upon first glance, we can see strings that reveal its nature—this sample didn’t expect anyone to reach this point, as it has three well-defined phases that conceal its tracks, but here we can see many indicators of what it is.

Overview of the extracted HawkEye (Image 1)
![{ } Debugger •4 Clipboard 00200000C Base Type and Interfaces Derived Types .ctoro: void @0600005E ChangeCIipboardChain(IntPtr, IntPtr) : bool 00600005A : void 006000062 : void 00600005F SendMessage(IntPtr, int, IntPtr, IntPtr): long 006000058 SetClipboardViewer(1ntPtI) : IntPtr 006000059 UninstallO : void 006000060 WndProc(ref void 006000061 Changed : Clipboard.ChangedEventHandIer 014000001 ID : Intptr 0040000CA ChangedEventHandIer 002000000 Debugger 002000008 RunPE@02000011 Base Type and Interfaces Derived Types .ctoro: void 006000072 CreatePrccessA(ref string, String8uiIder, IntPtr, IntPtr, bool, int, IntPt GetThreadContext(1ntPtr, uint[]): bool @0600007A NtlJnmapViewOfSection(IntPtr, IntPtr) : uint 006000079 : void 00600007C ReadProcessMemory(IntPtr, IntPtr, ref IntPtr, IntPtr, ref IntPtr) : bool int 006000077 SetThreadContext(1ntPtr, uint[]): bool 006000076 VirtualAIIocEx(IntPtr, IntPtr, IntPtr, int, int) : IntPtr 006000075 VirtualProtectEx(IntPtr, IntPtr, IntPtr, int, ref int): bool 006000074 WriteProcessMemory(IntPtr, IntPtr, byte[], IntPtr, ref IntPtr) : bool Cd](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXdq6a0KrJjiNN-sc0W9k9iQmGJjvicW8-YmfQhf-K9M9PWCfEeqUrvLtIOfZ8eym6fL5xgfQPSL_XXtT64tiv2KjT9mjHKKfBdOUHGzuPldw7YRMzwmS5tx6Dut3Uf6a22PeLf9AKUSh1WN0_xUEAY?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Overview of the extracted HawkEye (Image 2)
During the execution of this specific module, we can observe it invoking vbc.exe as it injects the payload into this process, using the same techniques we’ve previously seen.

Execution of HawkEye’s final stage (Image 1)

Execution of HawkEye’s final stage (Image 2)
![RunPE 002000011 Base Type and Interfaces Derived Types .ctoro: void 006000072 CreatePrccessA(ref string, String8uiIder, IntPtr, IntPtr, GetThreadContext(1ntPtr, uint[]): bool @0600007A NtlJnmapViewOfSection(IntPtr, IntPtr) : uint 00600007! : void ReadProcessMemory(IntPtr, IntPtr, ref IntPtr, IntPtr, ref int 006000077 SetThreadContext(1ntPtr, uint[]): bool 006000076 VirtualAIIocEx(IntPtr, IntPtr, IntPtr, int, int) : IntPtr 0060 VirtualProtectEx(IntPtr, IntPtr, IntPtr, int, ref int): bool WriteProcessMemory(IntPtr, IntPtr, by-ten, IntPtr, ref Inl](https://lh7-rt.googleusercontent.com/docsz/AD_4nXdiTsJymcbOYOrpzMZZ8dg-hiM_nRgz24UjQp8_W26v9jbcBm6ARPilw5YJ5la5lRe9vKxn52s0v6tPIAP_f02kEHENcfBa9y5EnnATliM-FbLWReIKn3qBVo5-6tI1AJIRn7M6dA1xgwbRslrqDA?key=dPMtnkS0P_zRmxCSZc1vAHMi)
Execution of HawkEye’s final stage (Image 3)
Regarding the modules it brings, I compared three different samples, and they are quite similar in terms of what they can do. The general functionalities that typically match include:
- Keylogging (Monitoring and stealing keyboard and clipboard data)
- System information gathering (OS, HW, Network)
- Credential theft (Mail, FTP, browsers, video games, etc.)
- Wallet theft
- Screenshot capture
- Security software detection
- Analysis tools detection (Dbg, traffic, etc.)
- Persistence (usually via registry keys or Tasks)
- Information exfiltration through various methods (FTP, HTTP, SMTP, etc.)
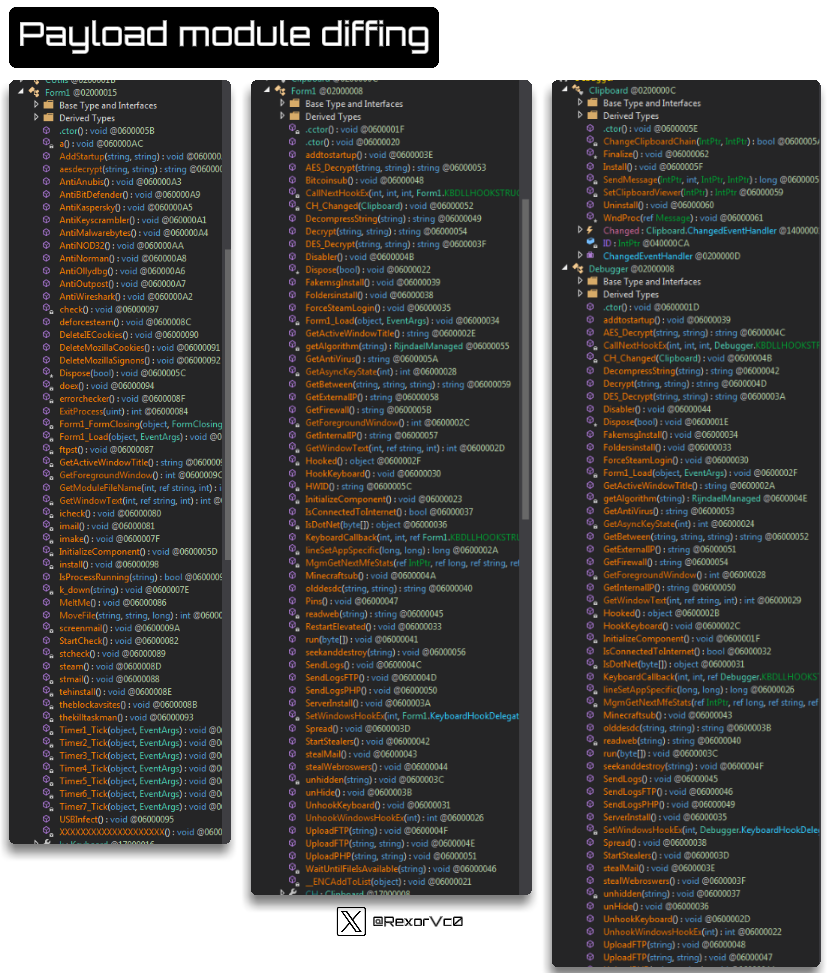
Graph of payload module diffing
Calling HawkEye a keylogger is really an oversimplification, as it performs more functions than many stealers I’ve seen. Once injected into vbc.exe or other processes, it carries out various actions mentioned above.
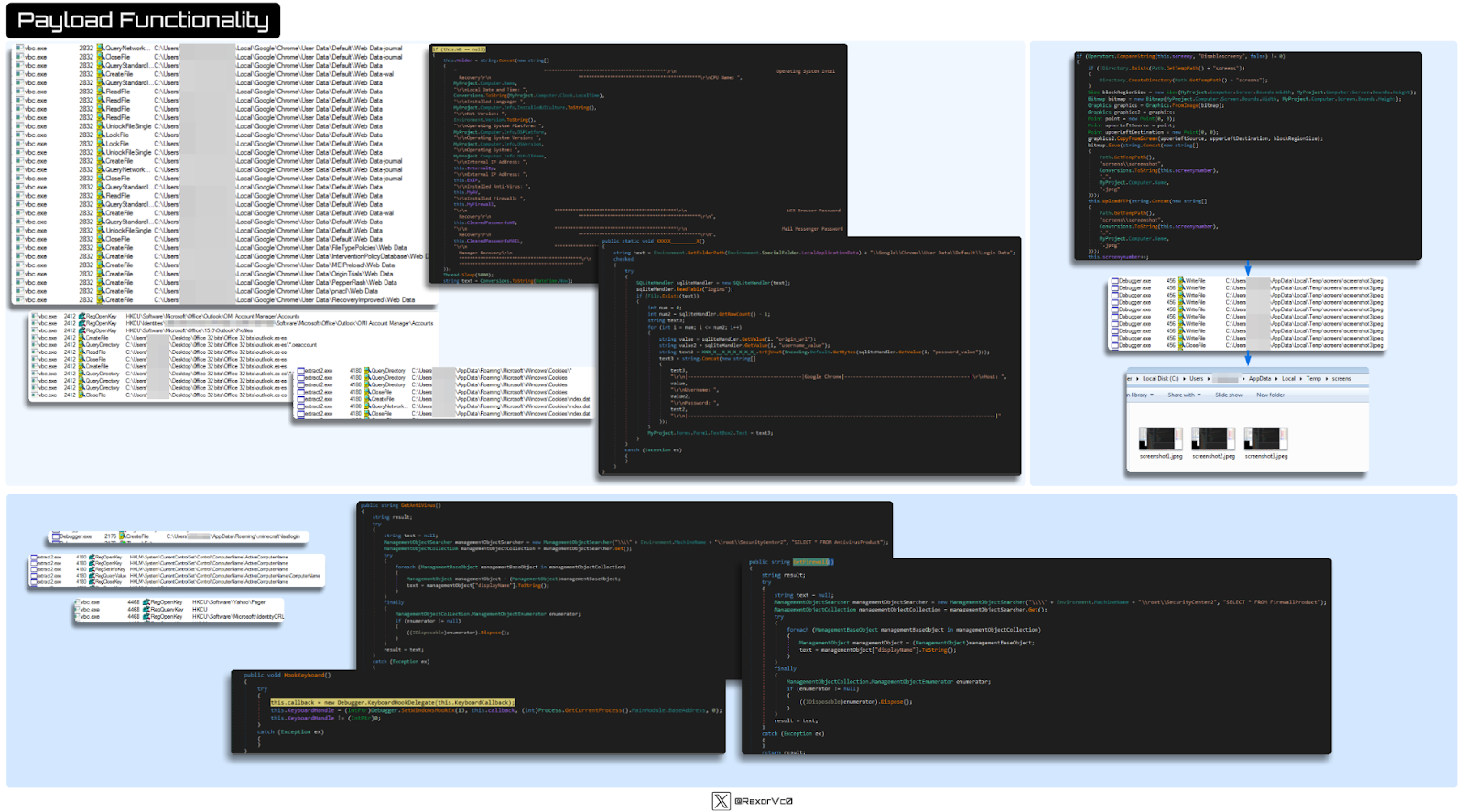
Graph of HawkEye functionality
Outro
As we discussed earlier, different groups have used this keylogger, as well as independent criminals or even script kiddies. In my research, I found different places where this keylogger was sold—there were up to 4-5 different sites, as it changed developers and domains over time, which is quite common.

HawkEye webpage
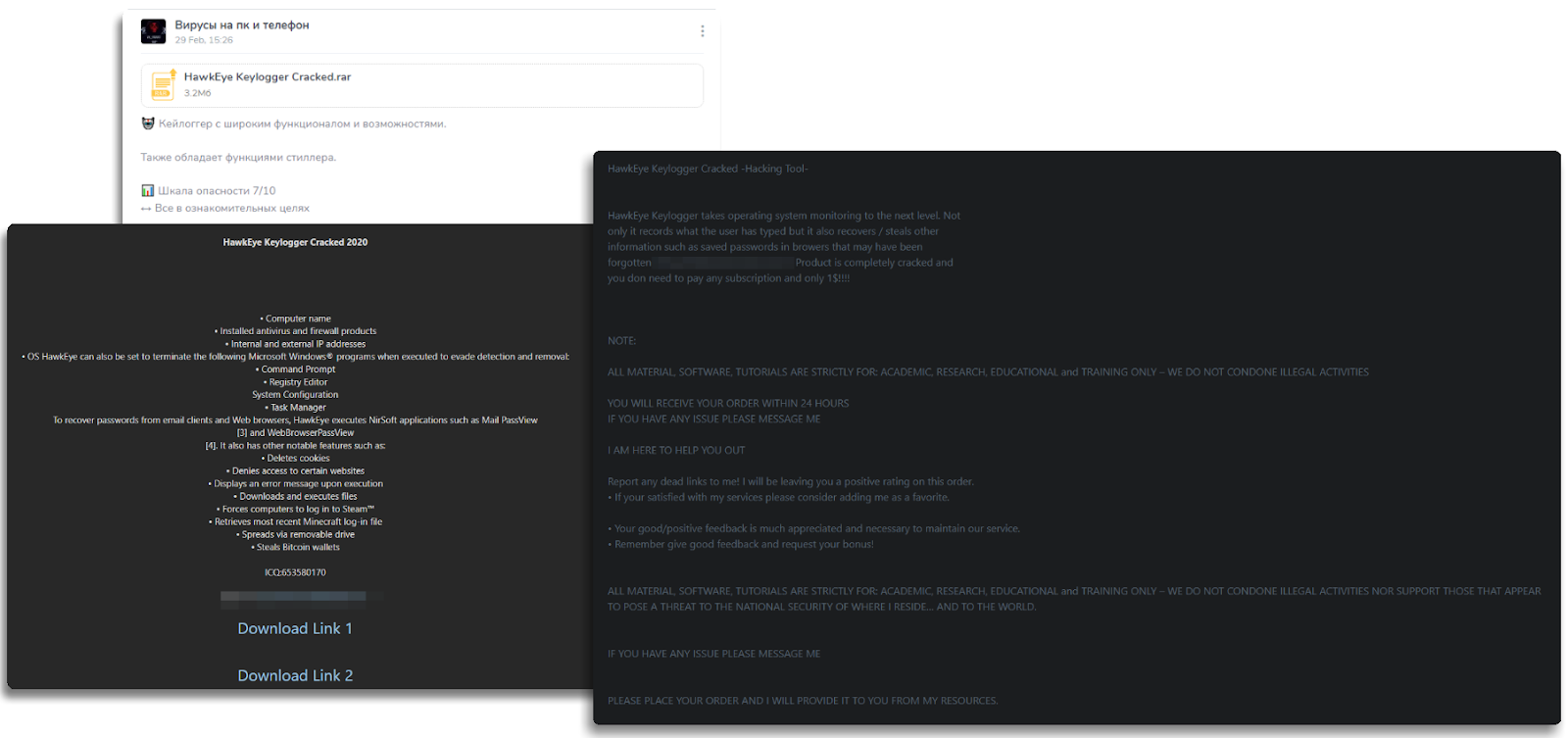
HawkEye product sales
It’s always important with these kinds of tools to locate the original software in different versions to understand how it works from both the victim’s and the attacker’s perspectives, so we can get a complete view of the malware.
Here, we can see that the builder provides a multitude of configuration options, allowing us to choose where to send the stolen information (email, FTP, etc.), what we want to collect (browser info, FTP credentials, mail, etc.), whether to check for certain tools, establish persistence, delete data, download from a domain (this could function as a downloader for other malware), change the payload data to make it appear like legitimate software (e.g., changing the icon, description, etc.). As you can see, it’s incredibly comprehensive. After compiling, we’ll have our complete Keylogger, Stealer, or Downloader (call it what you will, as it does everything) ready to use.

Graph of HawkEye builder
I don’t want to repeat myself too much, but when comparing the versions we’ve seen and extracted with the ones we created ourselves, they function exactly the same—same injections, persistence, data theft (or whatever was chosen in the builder). Therefore, in telemetry, we won’t find any surprises, as you can see below.
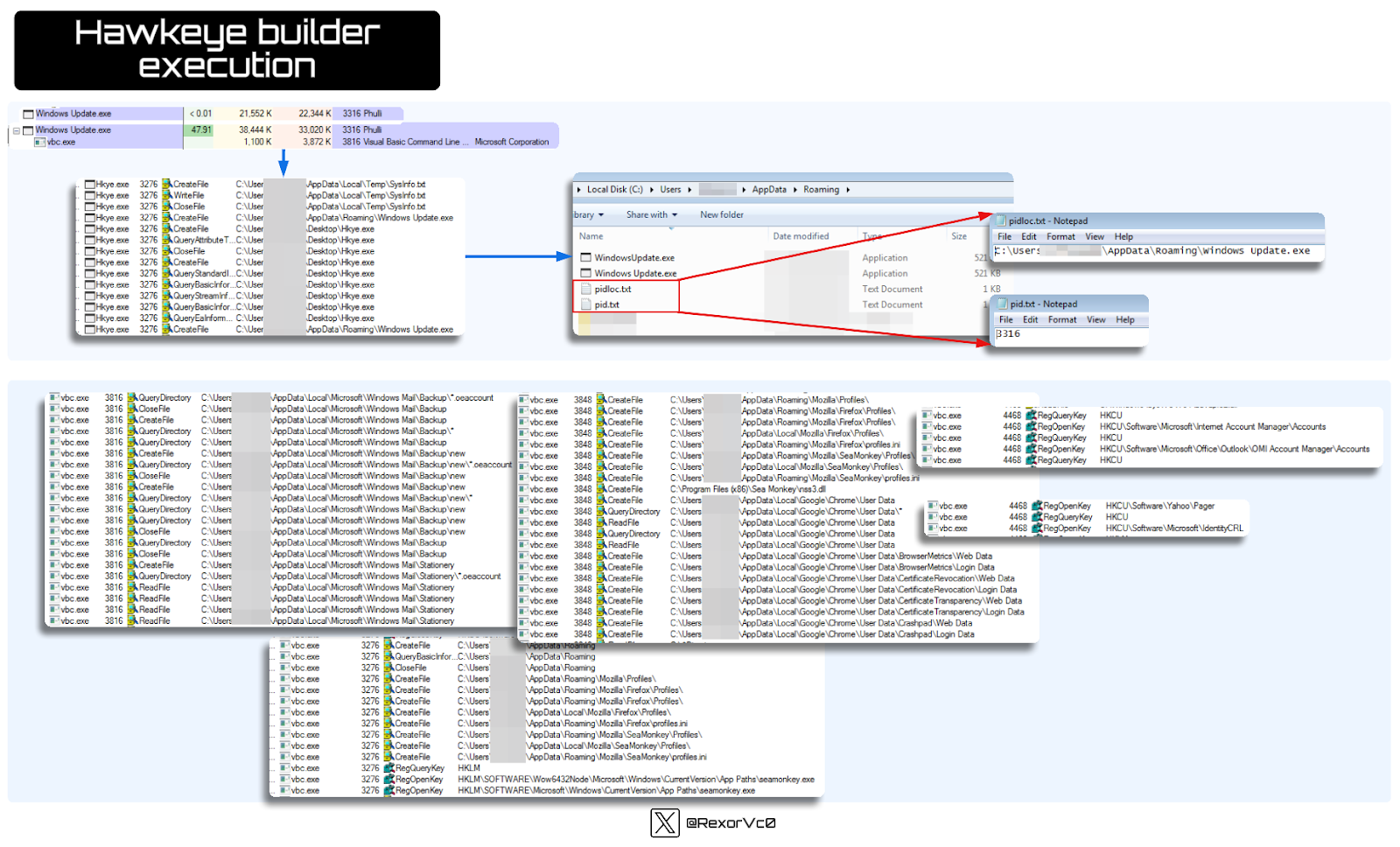
Graph of HawkEye builded execution
After analyzing all of this, I hope you are as impressed as I am by the sheer versatility and longevity HawkEye has displayed over the decades. It’s truly a tremendously powerful and easy-to-use tool that, unfortunately, we will continue to see in security incidents from actors of all types.
The post HawkEye Malware: Technical Analysis appeared first on Cybersecurity Insiders.
November 29, 2024 at 11:18AM










