Introduction
Companies are increasingly pursuing a cloud-first strategy by developing and deploying applications with the cloud in mind. With the majority of organizations adopting a hybrid or multi-cloud approach to support various use cases and work models, the attack surface has significantly broadened, making securing today’s cloud environments more critical and increasingly complex.
The 2024 Cloud Security Report, based on a comprehensive survey of 927 cybersecurity professionals worldwide, provides critical insights into the current trends driving cloud security. It explores key challenges in protecting complex cloud environments, what solutions and strategies cybersecurity professionals are prioritizing, how they’re allocating their resources, and the best practices they’re adopting to ensure the security of cloud workloads.
Key findings include:
- Multi-Cloud Preference: A majority of organizations (78%) opt for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to combine flexibility, control, and the unique benefits of various cloud services.
- Cloud Adoption Barriers: Security and compliance concerns (59%) are critical roadblocks to faster adoption of multi-cloud strategies. Technical challenges (52%) and resource constraints (49%) present substantial challenges in achieving visibility and policy control within complex multi-cloud infrastructures and emphasize the necessity for robust cloud security expertise.
- Cybersecurity Talent Shortage: Companies face a critical shortage of cybersecurity expertise, with 93% of respondents concerned about finding qualified professionals to protect complex multi-cloud environments. This directly affects their security posture and strategic efforts. This persistent scarcity of cloud security expertise hinders faster and more widespread adoption of multi-cloud strategies.
- Unified Cloud Security Platform Preference: 95% of respondents advocate for a single platform to streamline security across cloud environments. The objective is to simplify and automate security management, mitigate the talent gap, and enhance security through consistent policy enforcement and visibility, addressing the inefficiencies of managing multiple disparate security systems.
We would like to thank Fortinet for the invaluable support of this important industry research project. We hope this report serves as a practical guide for cybersecurity leaders and practitioners to navigate the complexities of cloud security more effectively in your ongoing efforts to secure your organization’s cloud journey against evolving cyber threats.
Thank you,
Holger Schulze Founder
Cybersecurity Insiders
Cloud Deployment Strategies
Choosing the right cloud deployment strategy is critical for organizations to maximize the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing associated risks.
The majority of organizations (78%) favor a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy, integrating multiple deployments into a single operating environment. A large portion of this (43%) use a hybrid of cloud and on-premises infrastructure. 35% of organizations have a multi-cloud strategy, highlighting a preference for leveraging the strengths of different cloud service providers for a variety of use cases. Just 22% rely on a single cloud provider, suggesting a focused approach that simplifies management but that may increase dependency on one vendor.
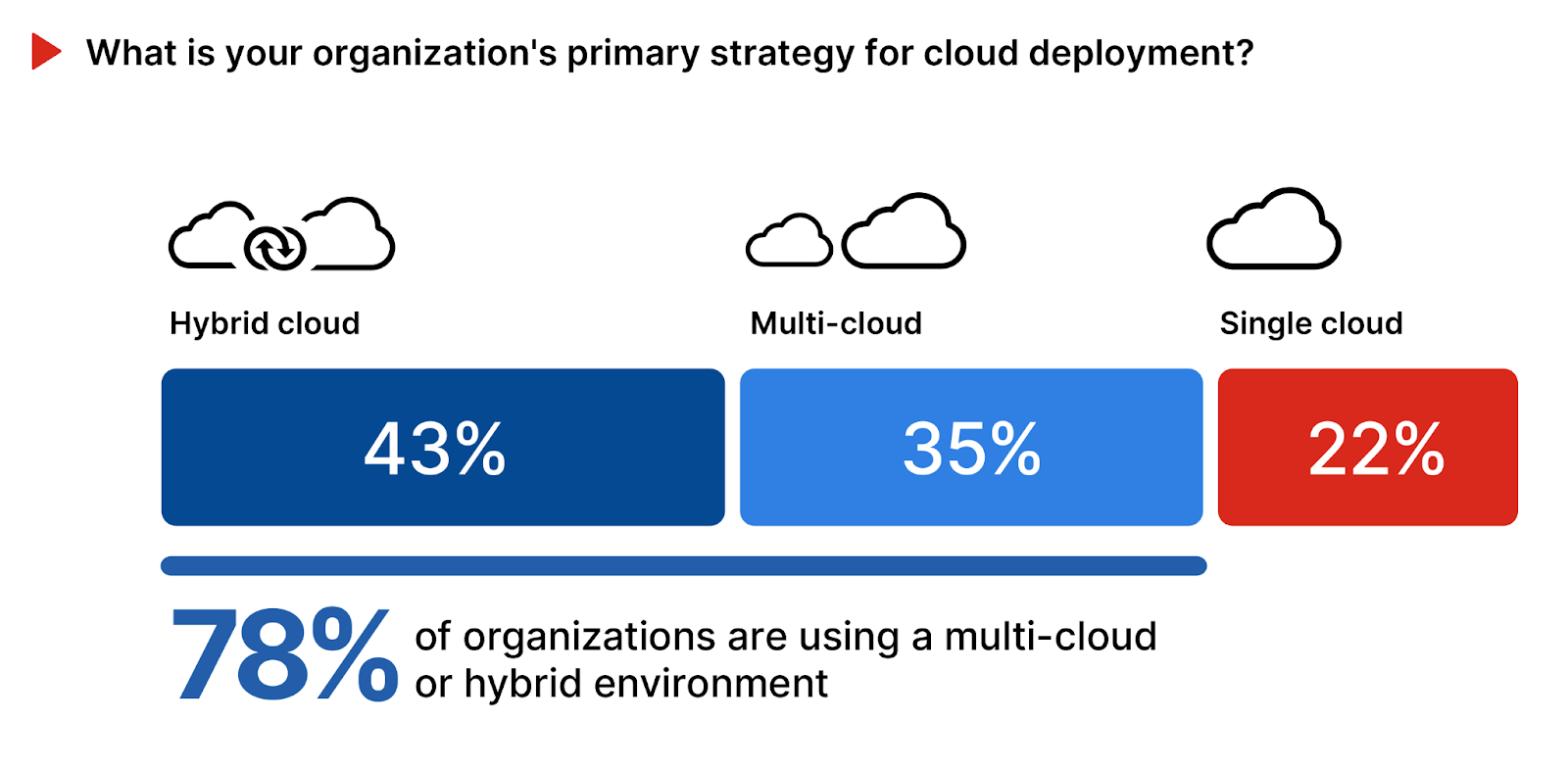
To better navigate the complexities of hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, organizations should prioritize an integrated security framework that ensures seamless protection across their entire digital footprint. This is essential to delivering the agility, scale, and security needed for robust defense against evolving cyber threats.
Multi-Cloud Adoption
The number of cloud providers an organization uses is crucial, impacting operational flexibility, risk management, and the complexity of security implementations. A majority of organizations (71%) use two or more cloud providers, indicating an approach that seeks to combine flexibility, control, and the unique benefits of each cloud service provider. An increase of 2 percentage points from last year’s survey reflects a growing shift towards multi-cloud strategies, driven by the need for specialized cloud services, regional availability, and redundancy.
Interestingly, only 29% of organizations rely on just one cloud provider, highlighting a preference for simplicity and perhaps a strategic partnership with a single cloud provider.
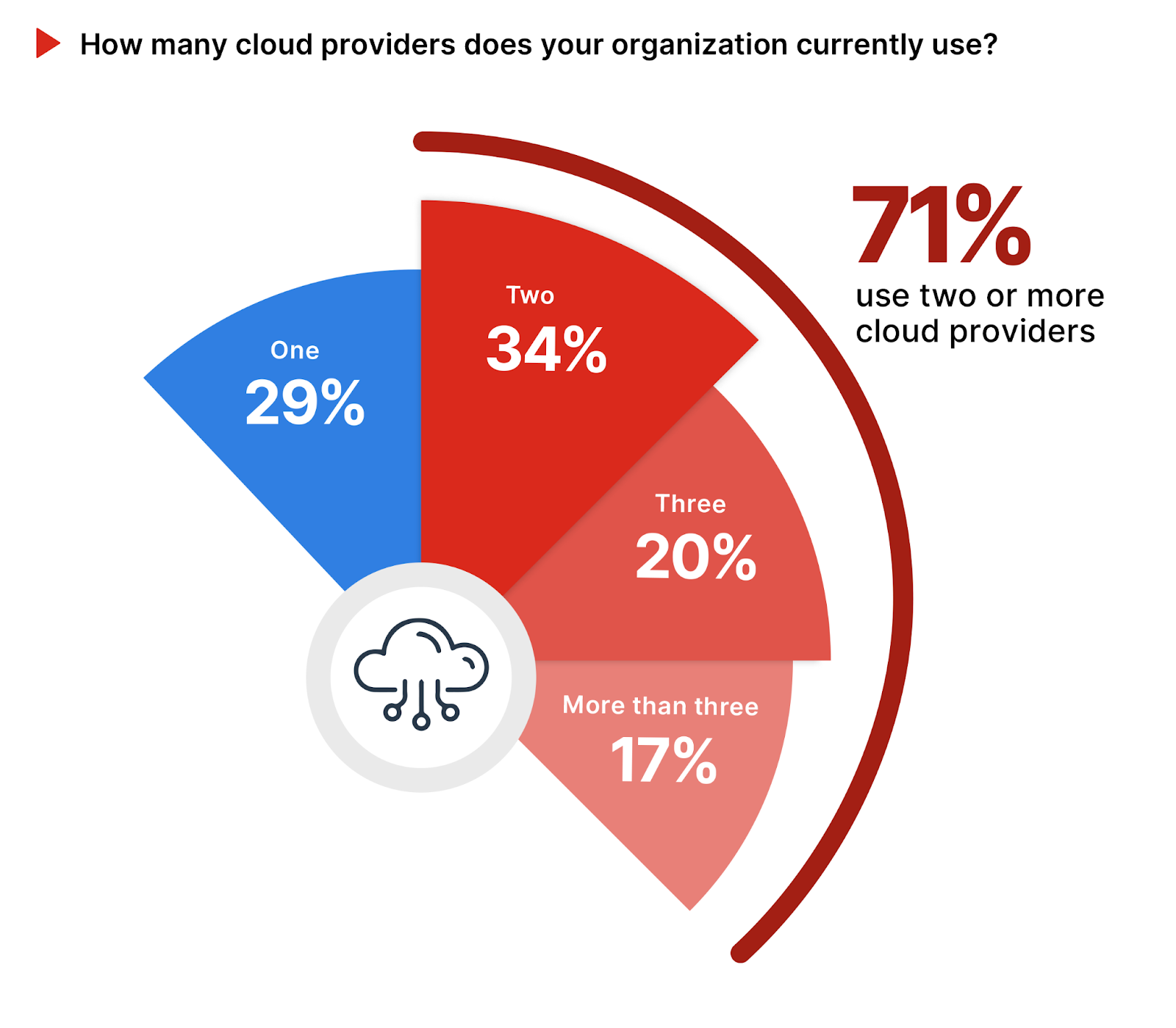
Organizations should adopt a seamless, cloud-neutral approach to securing multiple cloud environments that ensures consistent security policies and visibility across their digital footprint, reducing complexity and bolstering defense mechanisms against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Preferred Cloud Providers
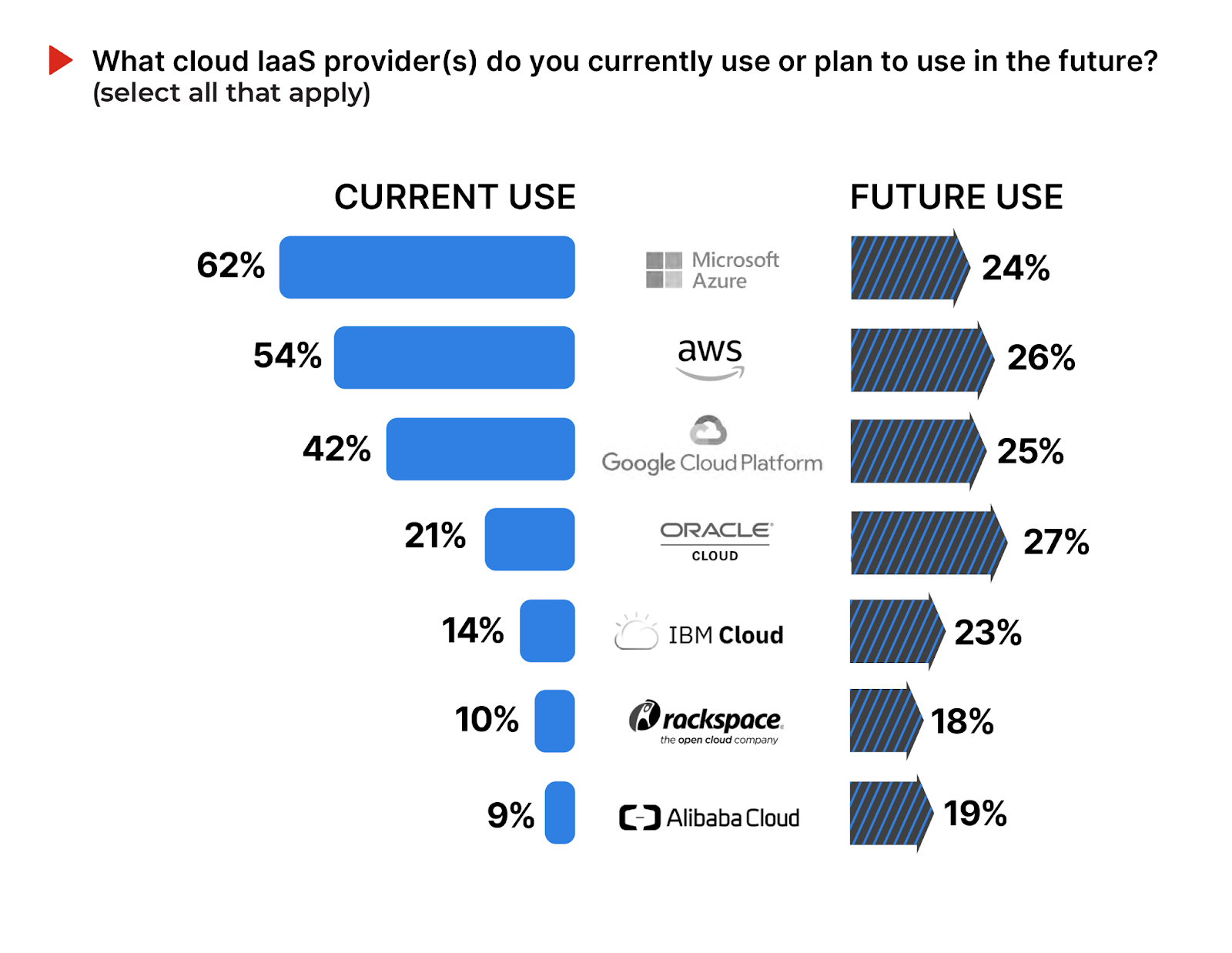
Next, we asked cybersecurity professionals about their current and future use of cloud providers, to better understand the changing market dynamics within the cloud ecosystem. Microsoft Azure continues to lead the market, with 62% of organizations in our survey currently utilizing its services, followed by Amazon Web Services (AWS) at 54%. This indicates a strong preference for these established cloud giants.
The survey results also highlight a significant interest in future adoption across all providers, particularly Oracle Cloud and Google Cloud Platform, with 27% and 25% of respondents planning to adopt these services, respectively. This suggests an increasingly diverse cloud adoption.
Navigating Cloud Adoption Barriers
Identifying and understanding the barriers to faster and more widespread cloud adoption is essential for organizations to better navigate the complexities of transitioning to cloud-based solutions.
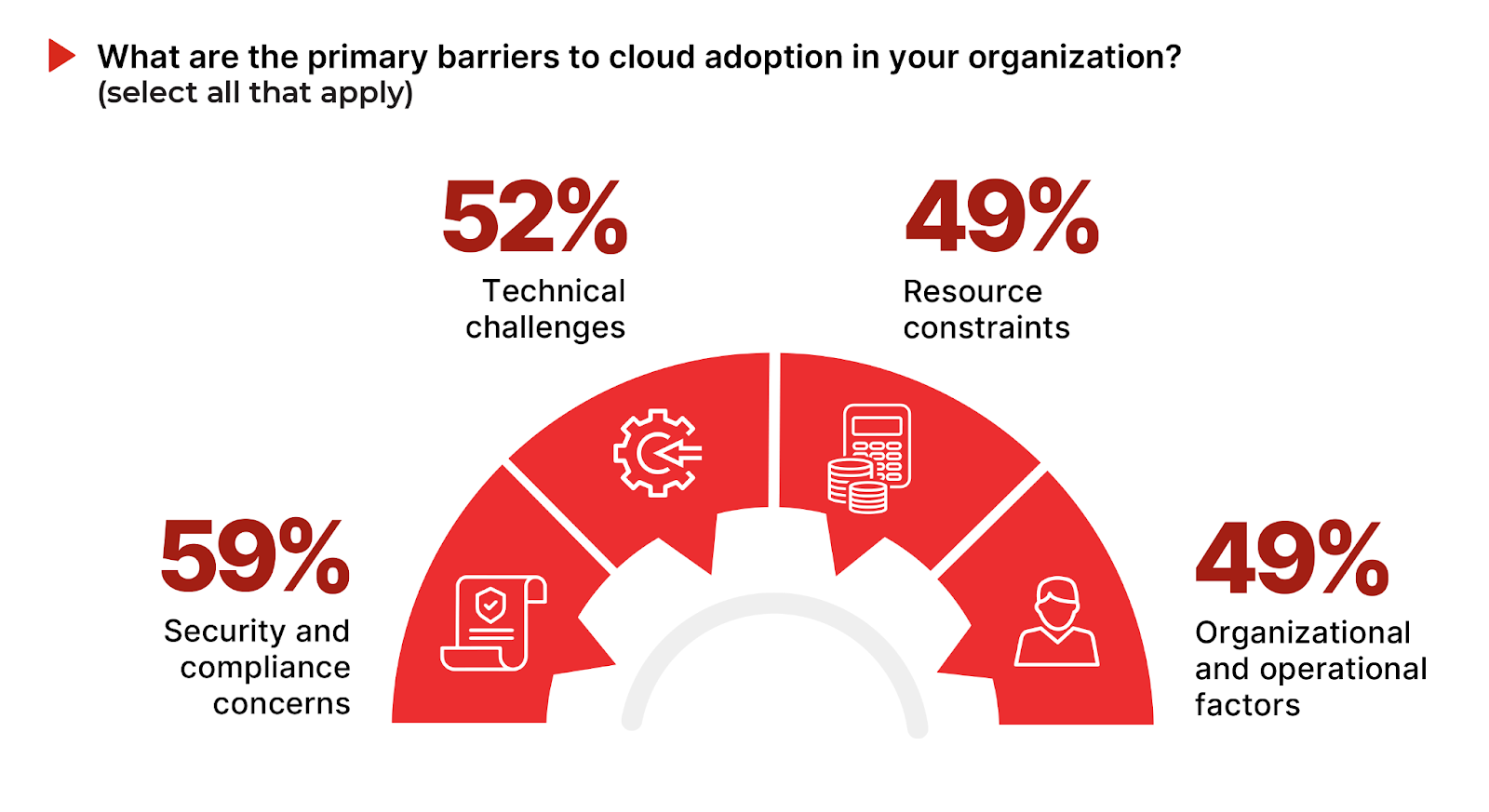
Security and compliance concerns are at the forefront, with 59% of respondents identifying it as a primary barrier. This highlights the importance of ensuring that security and compliance are an integral element of cloud adoption. Technical challenges follow closely at 52%, highlighting that the ease of cloud adoption is not without its challenges.
49% of respondents cite resource constraints, including the lack of staff expertise and budget limitations, underscoring the need for adequate investment in human and financial resources to support cloud initiatives. Organizational and operational barriers (49%) underscore that cloud computing is not just a new technology, it is also a new operating model that offers innovative working methods and requires management buy-in to address potential resistance to change.
Perceptions of Cloud Security Risks
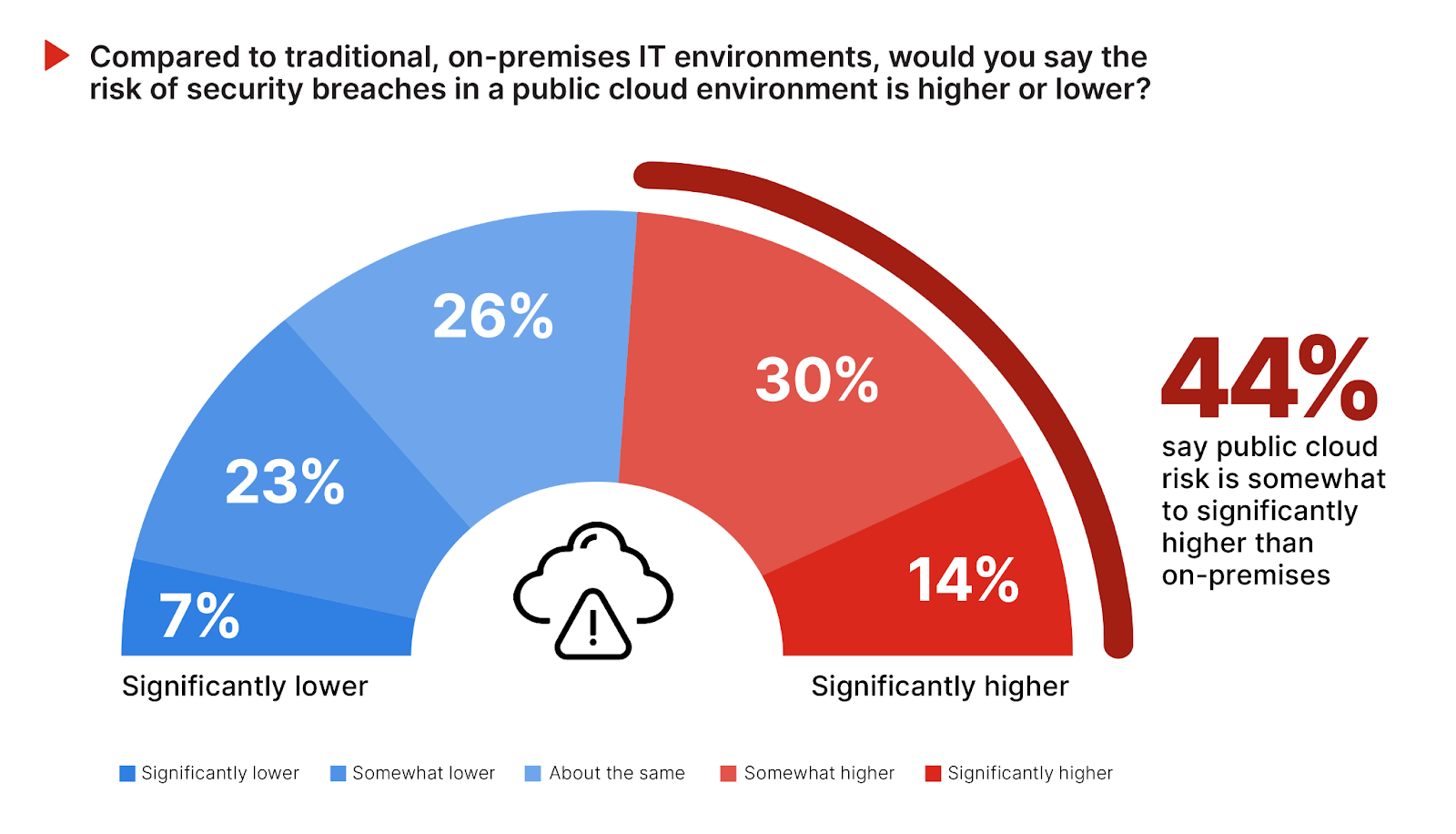
Evaluating the risk of security breaches in public cloud environments reveals significant concerns about the risks and unique security challenges associated with cloud computing, compared to on-premises environments.
A combined 44% of respondents perceive the risk of security breaches in public cloud environments as higher than in traditional on-premises IT environments, with 30% considering it somewhat higher and 14% viewing it as significantly higher.
Conversely, 30% of participants view the risk as lower in public cloud environments, indicating confidence in cloud providers’ security measures and advancements. A notable 26% of respondents believe the risk remains the same, suggesting that while the cloud introduces new dynamics, the fundamental security challenges persist across environments.
Public cloud offers organizations the opportunity to embrace a proactive, automated approach to security. Adopting a security-by-design mindset offers organizations the ability to effectively mitigate risks and capitalize on the scalability, flexibility, and innovation that the cloud offers.
Cloud Security Concerns
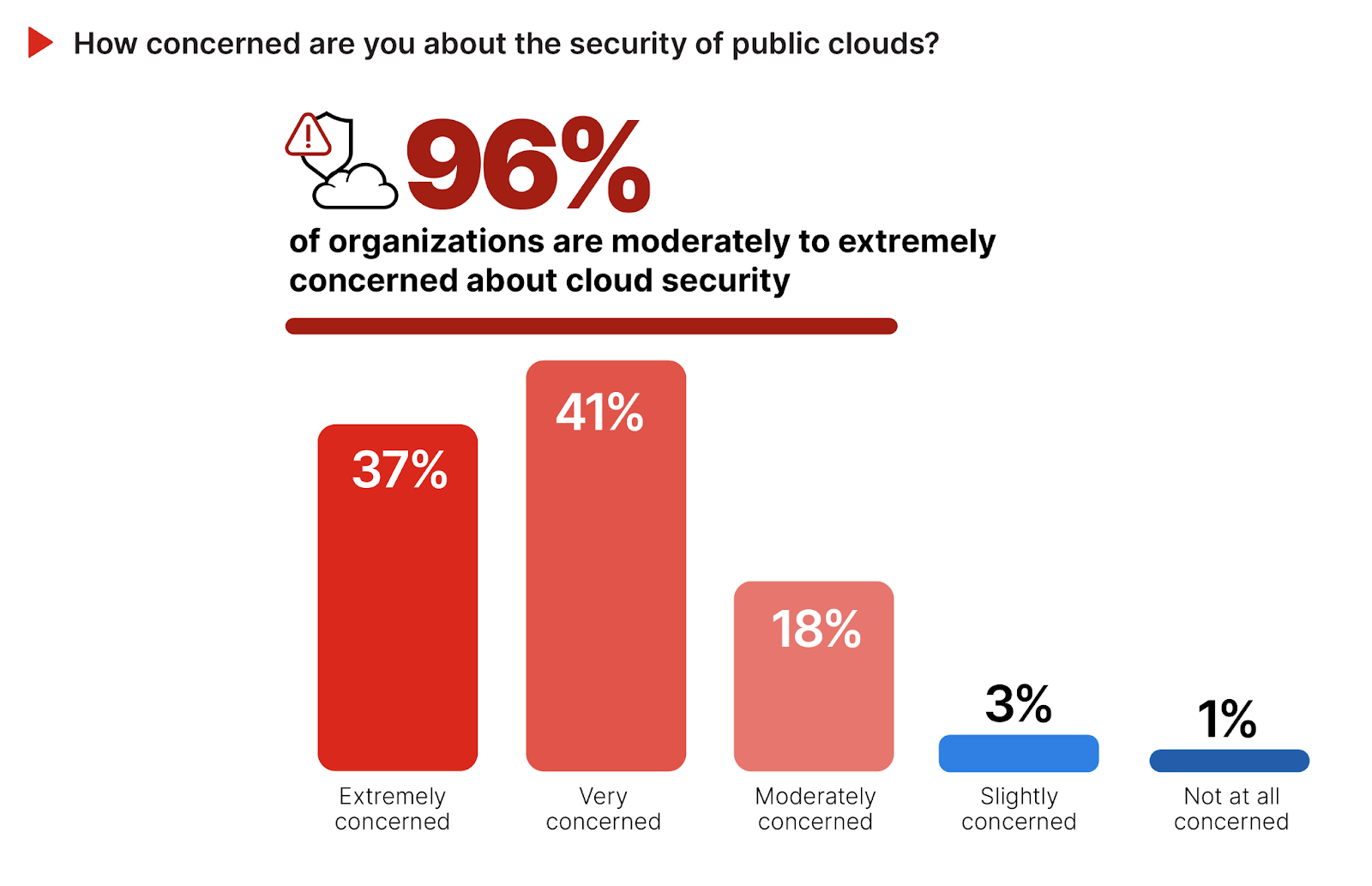
The level of concern regarding public cloud security is a critical indicator of the cybersecurity community’s perception and readiness to address potential risks and threats.
Despite increasing cloud adoption, cloud security concerns show no signs of improving: a significant majority of 96% express high levels of concern, with 37% being extremely concerned and 41% very concerned about public cloud security. The high degree of cybersecurity concern, which has remained consistent over the years, acts as a significant barrier to faster cloud adoption, as organizations grapple with the perceived risks and the complexities of securing cloud environments. Only a small fraction (22%) report moderate to no concern, indicating a strong consensus on the importance of robust security measures in public cloud deployments.
This data aligns with the previous finding where a combined 44% of respondents perceived a higher risk of security breaches in public clouds compared to traditional on-premises environments. This reinforces that while cloud computing offers numerous benefits and grows rapidly, security remains a paramount concern.
To address these concerns, organizations should not only maintain a security-by-design approach but also invest in continuous monitoring, threat intelligence, and incident response capabilities specific to cloud environments. Adopting cutting-edge security solutions and fostering strong collaborations with cloud providers can help mitigate the perceived risk and concerns associated with public cloud, ensuring a secure and resilient cloud infrastructure.
Challenges in Cloud Security Operations
The management of day-to-day cloud security operations presents a multifaceted challenge for organizations, requiring a delicate balance between technological, procedural, and human factors. Data security and privacy emerges as the top concern, with 58% of respondents highlighting the critical importance of protecting sensitive information and preventing data leaks in the cloud. This underscores the importance of robust data governance and encryption practices. Configuration management is a close second at 55%, reflecting the complexity and potential risks associated with cloud configurations—as a single misconfiguration can expose organizations to significant security risks.
Access control and identity management is another major challenge, cited by 54% of participants, emphasizing the need for stringent control over user access and privileges to prevent unauthorized access. Threat detection and respons (50%) and endpoint security (45%) further indicate the ongoing struggle to identify and mitigate security threats in real-time and secure the myriad of devices accessing cloud services. Policy and compliance management (45%) and cloud security management (45%) highlight the difficulties in ensuring consistent security policies across environments and aligning cloud security features with on-premises solutions.

To navigate these challenges in cloud security operations, organizations should prioritize a unified security strategy that leverages automation, advanced analytics, and integrated security platforms to streamline data security, policy enforcement, access management, and threat detection and response. Emphasizing the development of cloud-native security skills within teams and fostering a culture of security awareness can further enhance an organization’s ability to manage cloud security operations effectively.
Multi-Cloud Security Challenges
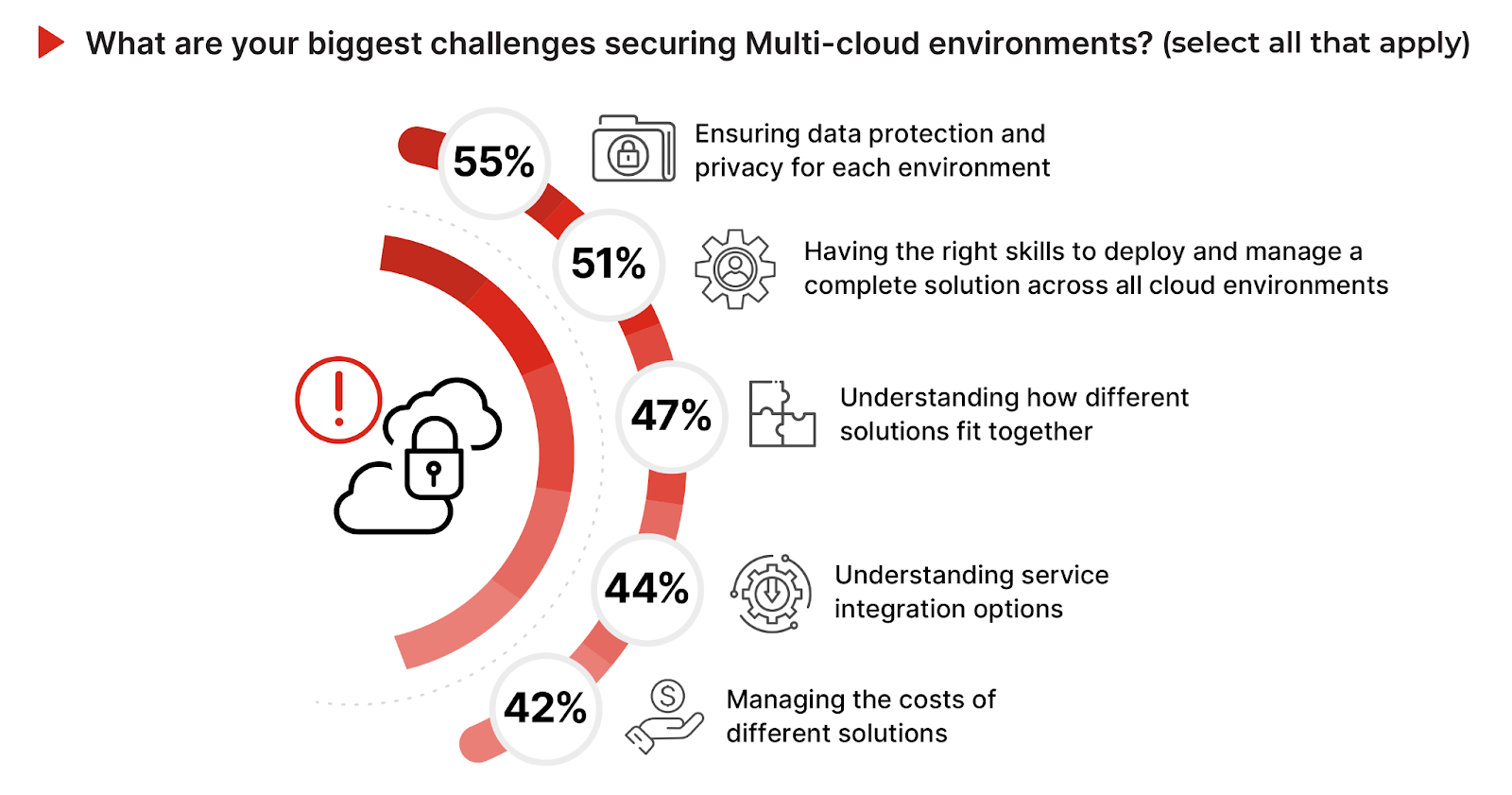
Multi-cloud environments significantly increase the complexity and challenges of securing cloud workloads. Ensuring data protection and privacy in each environment is identified as the most significant multi-cloud security challenge, with 55% of respondents highlighting it as a concern. This aligns with the earlier emphasis on data security and privacy as critical operational issues, underscoring the increased complexity when data is dispersed across multiple cloud environments.
Having the right skills to deploy and manage solutions across all cloud environments is a major challenge for 51% of participants, echoing the previously noted need for cloud-native security expertise to effectively navigate the multifaceted cloud security landscape. Understanding how different solutions fit together and understanding service integration options are critical challenges for 47% and 44% of respondents respectively.
These concerns spotlight the intricacies of achieving seamless integration and interoperability among diverse cloud environments, a crucial factor for maintaining robust security and operational efficiency. The challenge of managing the costs of different solutions, cited by 42% of respondents, further reflects the operational and financial balancing act required in a multi-cloud strategy.
To effectively address these challenges, organizations should leverage integrated security solutions that offer visibility and control across multi-cloud environments, supporting consistent data protection and privacy standards. Emphasizing partnerships with vendors that provide comprehensive multi-cloud security capabilities and fostering skills development can empower businesses to overcome the complexity of securing multi-cloud architectures. This approach not only mitigates the identified challenges but also harnesses the full potential of multi-cloud environments for enhanced agility, scalability, and innovation.
Cybersecurity Talent Gap
Echoing the challenges highlighted in securing multi-cloud environments, the ongoing shortage of skilled professionals capable of protecting complex multi-cloud environments stands out as an ongoing, critical industry problem.
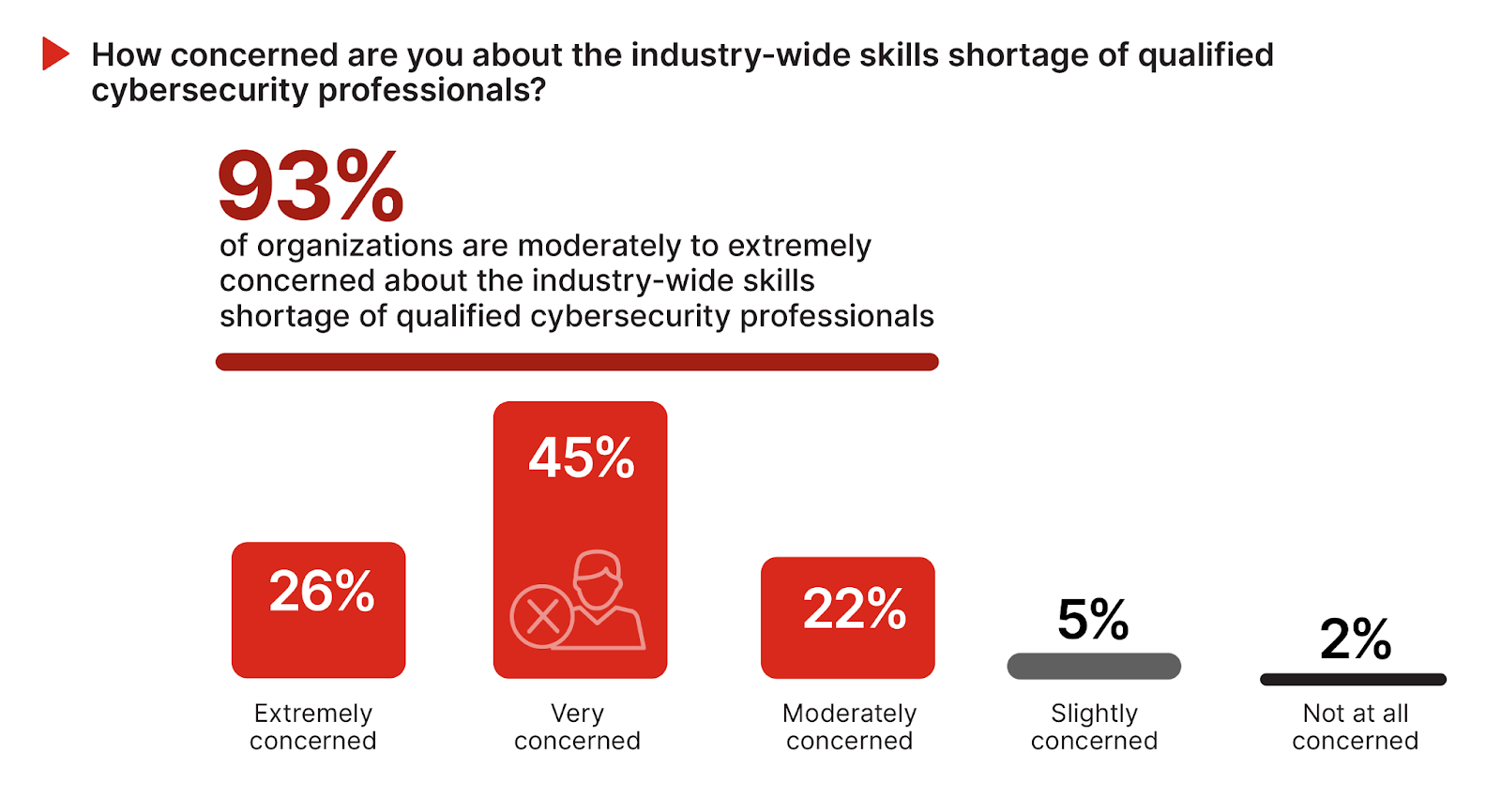
An overwhelming 93% of respondents express concern about the industry-wide shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals. This considerable apprehension reflects the acute awareness of the gap between the growing demand for skilled cybersecurity talent and the available workforce, a gap that exacerbates security vulnerabilities and operational challenges in an increasingly complex cyber landscape.
An emphatic 74% of respondents confirm that their organization is currently experiencing a shortage in cybersecurity talent. This finding quantifies the extent to which the skills shortage is affecting day-to-day security operations and strategic initiatives within organizations.
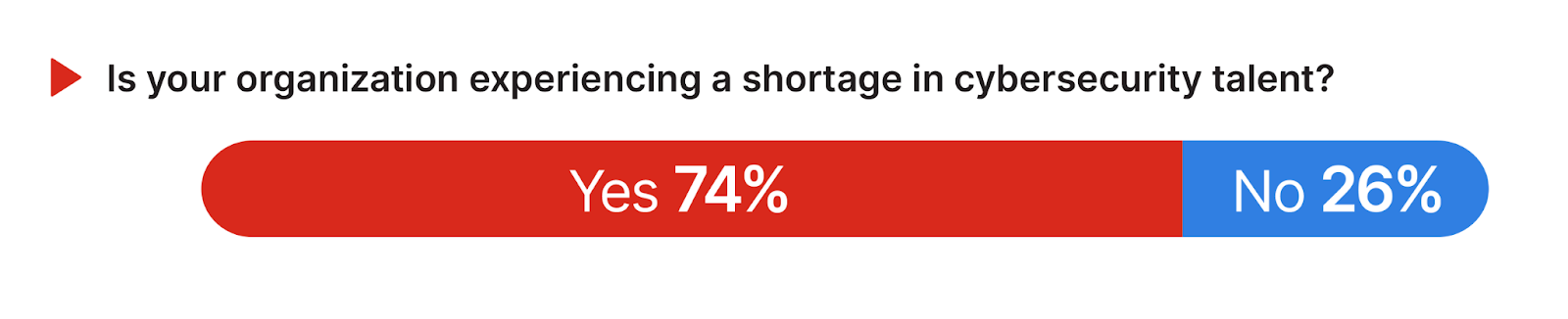
To mitigate the impact of the perennial cybersecurity skills shortage, organizations should consider a multifaceted approach that includes fostering partnerships with academic institutions to pipeline new talent and investing in training and development programs to cultivate internal talent and adapt to the evolving demands of cloud security. Organizations should also consider embracing unified security solutions that replace multiple-point solutions, incorporating artificial intelligence, and reducing operational complexity to bridge the skills gap while enhancing threat detection, response capabilities, and overall security posture.
Critical Cybersecurity Skills
In the context of the pronounced cybersecurity talent shortage faced by organizations, we asked about the specific cybersecurity skills deemed most critical for addressing today’s security challenges.
Cloud and application security skills takes the top spot, with 60% of respondents highlighting its critical importance. This underscores the accelerated migration to cloud services and the necessity for robust security practices in application development and deployment. Following closely, identity and access management (IAM) is identified by 59% of organizations as essential, reflecting the growing complexity of securing user access across increasingly distributed IT environments.
Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) is recognized by 58% of respondents as an important skill, underscoring the essential role of regulatory compliance and risk management frameworks in today’s cyber threat landscape. Security monitoring and operations, threat intelligence, and advanced technical security skills—all at 57%— demonstrate a nearly equal emphasis on proactive threat detection, understanding cyber adversaries, and leveraging advanced technologies for robust security posture.

Cloud Security Budget Trends
The allocation of resources to cloud security is a critical indicator of organizational priorities and the perceived importance of cloud infrastructure protection in the face of evolving cyber threats and technological advancements.
A significant 61% of respondents anticipate an increase in their cloud security budget over the next 12 months. This substantial majority signals a strong recognition of the escalating cybersecurity challenges and the need for enhanced security measures in cloud environments, propelling cloud security budget to increase by 37%.
The willingness to invest up to 37% more in cloud security reflects an understanding that robust defense mechanisms are essential to safeguard sensitive data and maintain compliance with regulatory standards in the increasingly cloud-centric business landscape.
Meanwhile, a third of organizations (32%) expect their cloud security budget to remain unchanged. Only a small fraction, 7%, project a decrease in their cloud security budget.
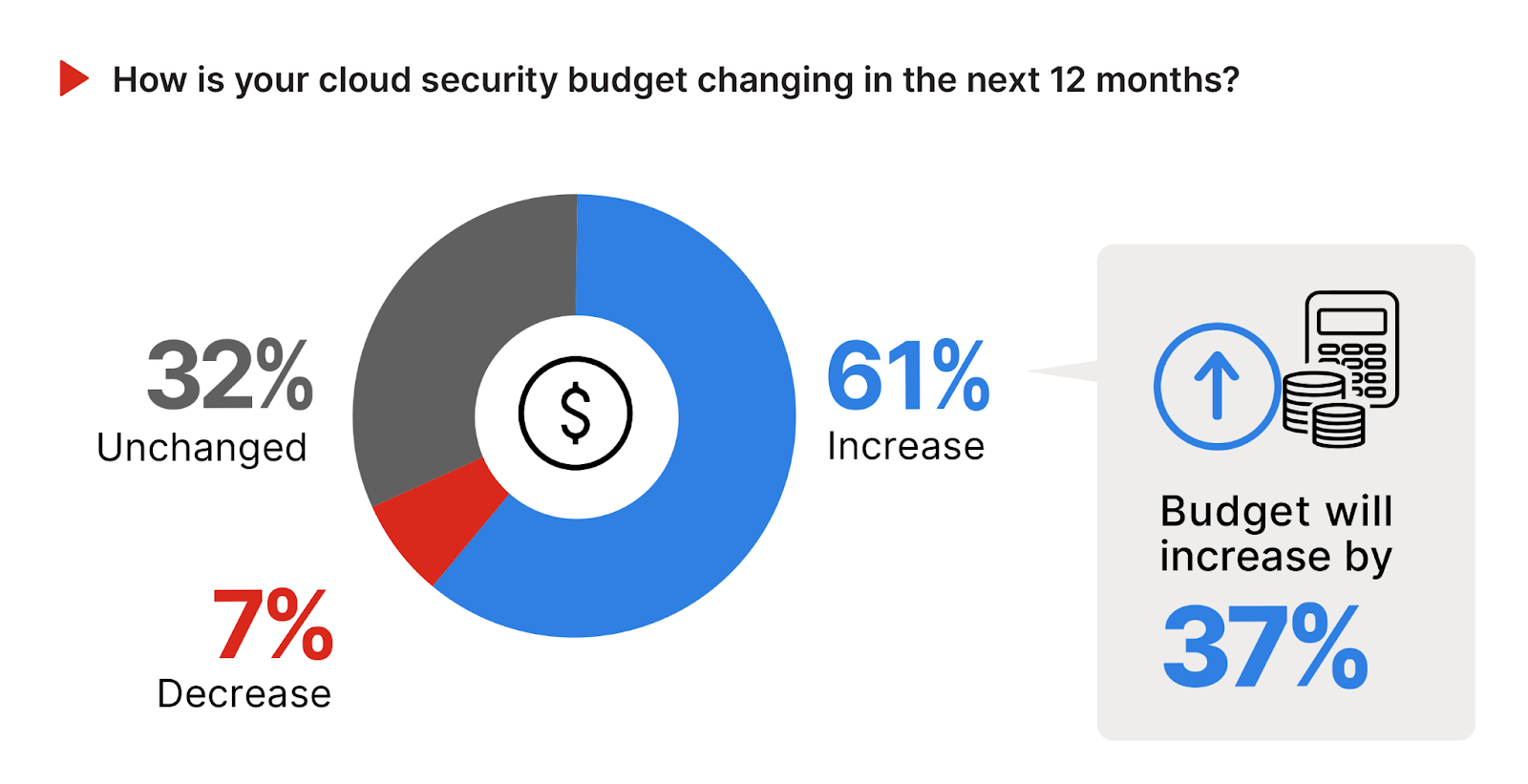
Given the predominant trend towards increased cloud security investment, organizations should strategically allocate additional resources to areas of highest risk and potential impact, such as advanced threat detection, identity and access management, and security automation. This approach not only prepares businesses to combat sophisticated cyber threats but also enhances their overall security posture by leveraging the latest technological innovations in cloud security.
Embracing Cloud-Based Security Solutions
The decision to adopt cloud-based security solutions is driven by a variety of factors that align with organizational goals for agility, efficiency, and enhanced protection. The need for better scalability, recognized by 56% of survey respondents, highlights the cloud’s ability to dynamically adjust to fluctuating demands. Close behind, cost savings and faster deployment, at 47% and 46% respectively, underscore the economic and operational benefits enticing organizations towards cloud security solutions. Enhanced performance (42%) and the reduction of manual efforts for patching and software upgrades (40%) further catalyze the shift to cloud-based security solutions, especially in light of the perennial cybersecurity skills shortage.
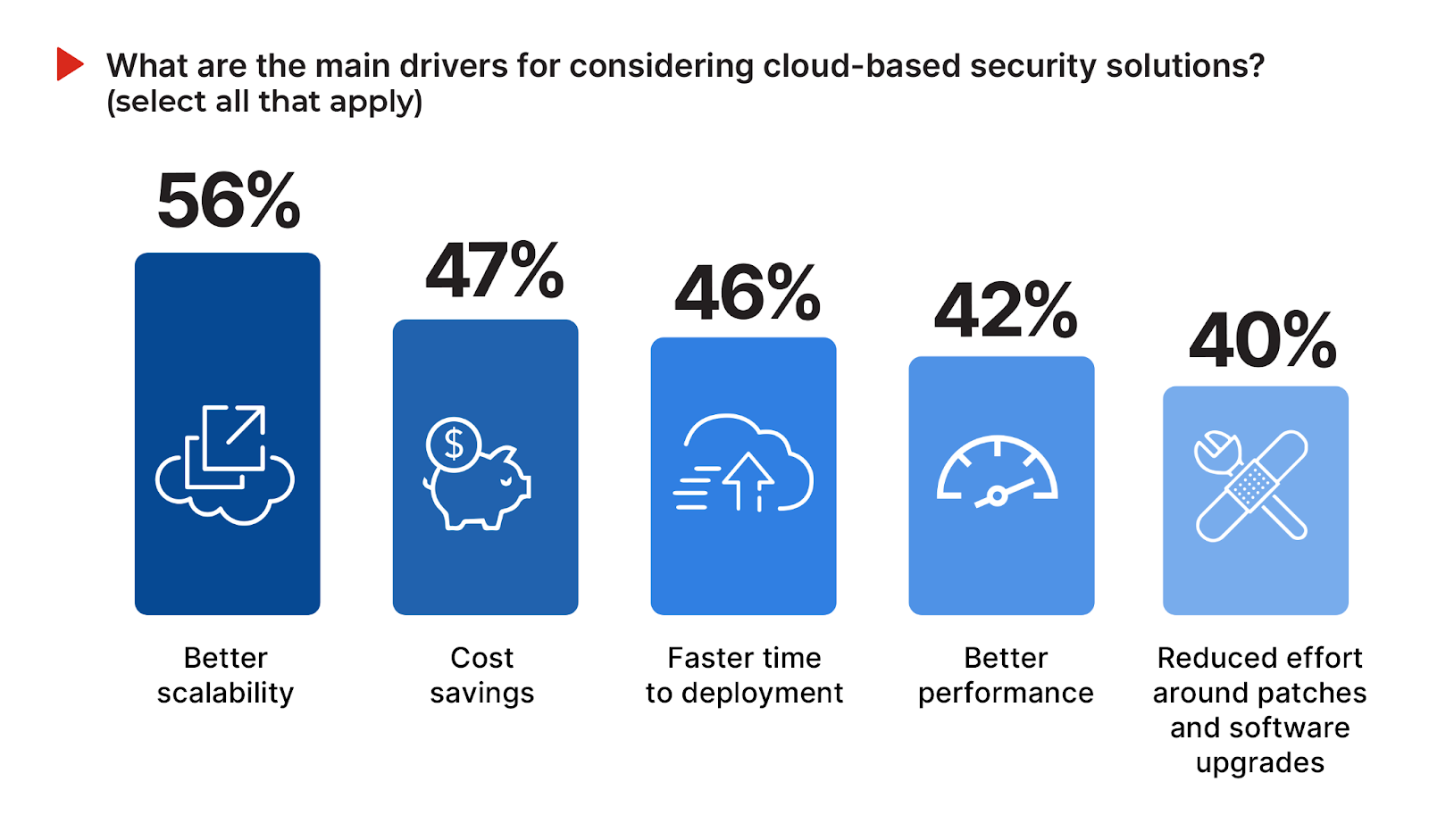
Organizations considering cloud-based security solutions should prioritize scalability, cost efficiency, and rapid deployment to capitalize on the cloud’s operational and economic advantages. Focusing on solutions that offer streamlined policy management and continuous compliance can further enhance security postures, ensuring resilience in the face of evolving threats and regulatory landscapes.
Unified Cloud Security Platform
Given the complexity, operational headaches, and skills challenges already highlighted, it comes as no surprise that organizations are looking for a unified security platform to streamline and consolidate security management across diverse cloud environments. An overwhelming 95% of respondents confirm that having such a platform would be advantageous for protecting data consistently and comprehensively across the cloud footprint.
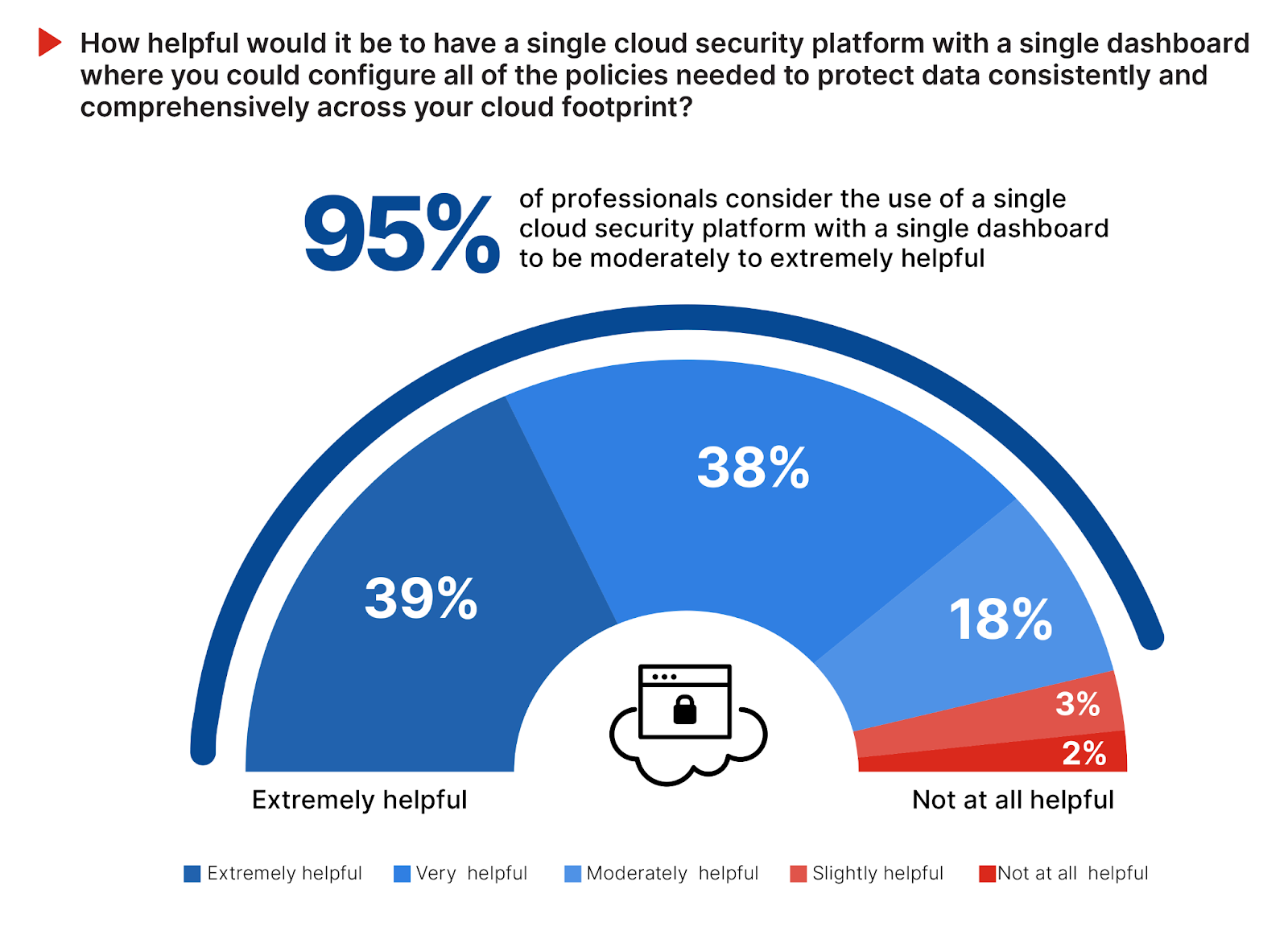
This demand for a single, integrated cloud security platform echoes the industry’s shift towards platform consolidation, driven by improving security effectiveness, simpler integration, and reduced management overhead. It is the only effective approach to addressing the cybersecurity talent gap and mitigating increasingly sophisticated and automated attacks. Such a unified platform alleviates the operational burden of navigating multiple security interfaces and enhances overall security posture through consistent policy enforcement and comprehensive visibility across all cloud environments.
Securely Embracing the Cloud: Essential Cloud Security Strategies
I n today’s rapidly evolving cloud landscape, adopting a robust cloud security posture is imperative for organizations of all sizes. This guide outlines essential best practices for securing your cloud environments, from unifying security platforms to investing in specialized skills, designed to protect against the sophisticated threats of tomorrow.
ADOPT A UNIFIED SECURITY PLATFORM: Centralize security control and visibility across all cloud environments to streamline operations and enhance visibility, a strategy preferred by 95% of organizations.
EMPHASIZE CLOUD-AGNOSTIC SECURITY: With 78% using hybrid or multi-cloud environments, it’s crucial to develop strategies that address the unique challenges of these environments and ensure consistent security policies and enforcement.
AUTOMATE POLICY AND COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT: Implement systems to automate and streamline security policies across cloud environments and consistently meet regulatory requirements.
PRIORITIZE DATA PROTECTION: Implement robust data governance and encryption to safeguard sensitive information across all cloud services, addressing the security challenge mentioned by 58% of organizations.
ENHANCE CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT: Actively manage cloud configurations to prevent misconfigurations and reduce exposure to security vulnerabilities.
STRENGTHEN ACCESS CONTROL: Employ strict identity and access management to implement Zero Trust principles and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
BOOST THREAT DETECTION AND RESPONSE: Leverage advanced analytics and automated response capabilities to identify and mitigate threats in real time.
INVEST IN CLOUD-NATIVE SECURITY SKILLS: With 93% expressing great concern over the cybersecurity skills shortage, foster the development of cloud-specific security expertise within your team to navigate the complex cloud security landscape more effectively.
Methodology and Demographics
The 2024 Cloud Security Report is based on a comprehensive global survey of 927 cybersecurity professionals conducted in February 2024, to uncover how cloud user organizations are adopting the cloud, how they see cloud security evolving, and what best practices IT cybersecurity leaders are prioritizing in their move to the cloud. The respondents range from technical executives to IT security practitioners, representing a balanced cross-section of organizations of varying sizes across multiple industries.
__
Fortinet (NASDAQ: FTNT) secures the largest enterprises, services providers, and government organizations around the world. Fortinet empowers our customers with complete visibility and control across the expanding attack surface and the power to take on ever-increasing performance requirements today and into the future. Only the Fortinet Security Fabric platform can address the most critical security challenges and protect data across the entire digital infrastructure, whether in networks, application, multi-cloud, or edge environments. Fortinet ranks #1 as the company with the most security appliances shipped worldwide and more than 730,000 customers trust Fortinet to protect their businesses. www.fortinet.com
__
Cybersecurity Insiders brings together 600,000+ IT security professionals and world-class technology vendors to facilitate smart problem-solving and collaboration in tackling today’s most critical cybersecurity challenges. Our approach focuses on creating and curating unique content that educates and informs cybersecurity professionals about the latest cybersecurity trends, solutions, and best practices. From comprehensive research studies and unbiased product reviews to practical e-guides, engaging webinars, and educational articles – we are committed to providing resources that provide evidence-based answers to today’s complex cybersecurity challenges. Contact us today to learn how Cybersecurity Insiders can help you stand out in a crowded market and boost demand, brand visibility, and thought leadership presence. Email us at info@cybersecurity-insiders.com or visit cybersecurity-insiders.
The post 2024 Cloud Security Report Fortinet appeared first on Cybersecurity Insiders.
December 26, 2024 at 12:59PM














 empowers security analysts to take immediate, decisive actions to mitigate impactful cyber exposures by taking advantage of unparalleled tactical attack surface intelligence.
empowers security analysts to take immediate, decisive actions to mitigate impactful cyber exposures by taking advantage of unparalleled tactical attack surface intelligence.