Exploring the Future of SASE, SSE, Zero Trust, and Hybrid Security Strategies
Overview
As organizations continue to manage increasingly sophisticated IT environments and widespread hybrid work models, the demand for secure, scalable network access remains a top priority. This 2025 Secure Network Access Report, based on insights from 411 IT leaders and cybersecurity professionals, explores the trends, challenges, and strategies that are shaping secure access today.
Key findings:
SASE Urgency Required: With 32% implementing, 31% evaluating, and 24% planning SASE adoption within the next year, momentum is building. However, with only 8% fully deployed, slow progress leaves organizations vulnerable, making it critical for distributed workforces to prioritize SASE for stronger security.
Remote Access as a Top Driver for SASE: 45% of participants identified secure remote and hybrid access for employees as their primary driver for adopting SASE solutions. This focus is vital, as 42% of respondents noted employees as the user group posing the greatest risk to business security. Traditional Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) often increase these risks, causing high latency, reduced performance, and inadequate security. SASE mitigates these issues with technologies like Software- Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN), optimizing traffic flow and performance while ensuring secure, seamless access for remote and hybrid employees.
Zero Trust on the Rise: With 38% of organizations currently implementing Zero Trust and another 42% planning to do so within the next year, this security model has become a key focus for managing access in distributed environments and reducing insider threats.
Challenges in SASE Implementation: 48% of respondents pointed to integration with existing systems as the most significant barrier to adopting SASE. Policy management across different environments (44%) and user disruption during transitions (38%) were also identified as common challenges. Managed services help address these integration challenges by connecting existing infrastructure with SASE components, ensuring minimal disruption and faster time-to-value.
Leveraging MSSPs to Address Expertise Gaps: 47% of respondents cited lack of in-house expertise as the primary reason for turning to Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs). Partnering with MSSPs can help streamline complex deployments like SASE, offering the expertise needed for seamless integration, improved network visibility, and reduced costs through a unified approach to security and performance.
This report provides in-depth analysis of these trends, alongside actionable recommendations for overcoming the challenges of SASE and Zero Trust implementation.
We extend our thanks to Hughes for supporting this critical research project. Their commitment to advancing secure access solutions has made this comprehensive analysis possible.
We hope that the insights provided in this report will guide your efforts to enhance security and protect your organization against evolving threats.
Holger Schulze
Founder, Cybersecurity Insiders
A Message from Hughes
Traditional IT approaches are a thing of the past as organizations navigate new and emerging technologies, workforce structures, and AI-driven cyber threats. In a world where the workforce is often distributed—and connected by cloud and other remote software solutions—securing a scalable network has never been more important. Cybersecurity as we know it is evolving, and we must evolve with it.
Thank you to all involved in this important research. As cybersecurity threats and technologies evolve, new partnerships and creative strategies will determine success and an organization’s ability to secure their workforce and safeguard their performance now and in the future.
Dan Rasmussen
SVP & GM, North America Enterprise Division, Hughes
Workforce Dynamics in a Hybrid World
The shift toward hybrid and remote models fundamentally impacts how cybersecurity strategies are deployed, particularly in securing network access, preventing insider threats, and managing distributed data environments.
With 63% of organizations now embracing a hybrid work model, maintaining secure access across a blend of remote and in-office environments has become increasingly critical. 19% of respondents operate fully remotely, further emphasizing the need for secure endpoint solutions and VPN alternatives.
Given the distributed nature of workforces, solutions like Security Service Edge (SSE) platforms offer layered protections, combining Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), and Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) to prevent data loss and ensure secure access. Managed Secure Access platforms are particularly valuable in simplifying these processes, providing centralized security management while ensuring high network performance.

Zero Trust Adoption: A Strategic Imperative
As organizations continue to face growing cyber threats, the adoption of Zero Trust security strategies has become increasingly critical for safeguarding networks, users, and data. Zero Trust, a framework that emphasizes continuous verification of identities and devices, has rapidly gained traction as a core security model for organizations aiming to reduce risk across their environments.
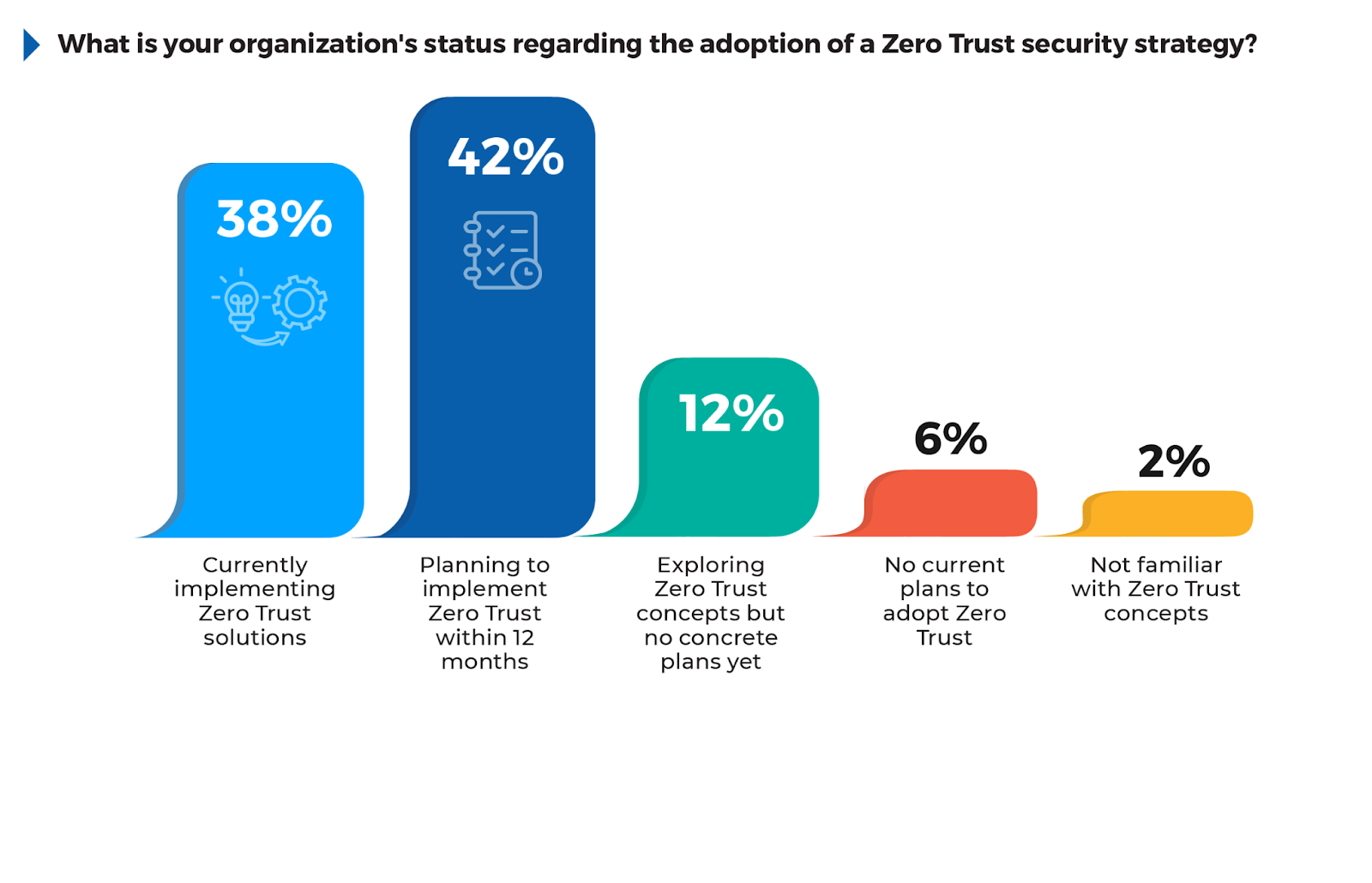
According to the survey, 42% of respondents are planning to implement Zero Trust within 12 months, showing that a significant number of organizations are in the early stages of their Zero Trust journey. 38% are currently implementing Zero Trust solutions, reflecting the urgency many organizations feel in transitioning to this security framework. The fact that 12% are still exploring Zero Trust concepts without concrete plans suggests that while awareness is high, some organizations are still evaluating how best to integrate these strategies into their infrastructure.
For organizations yet to adopt or fully implement Zero Trust, focusing on areas like Identity and Access Management (IAM), network micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring can provide immediate security improvements. Leveraging integrated Zero Trust solutions through managed service providers can further streamline adoption and reduce the complexity of deployment, ensuring a smoother transition while addressing the most critical security gaps.
Securing Access to Critical Business Resources
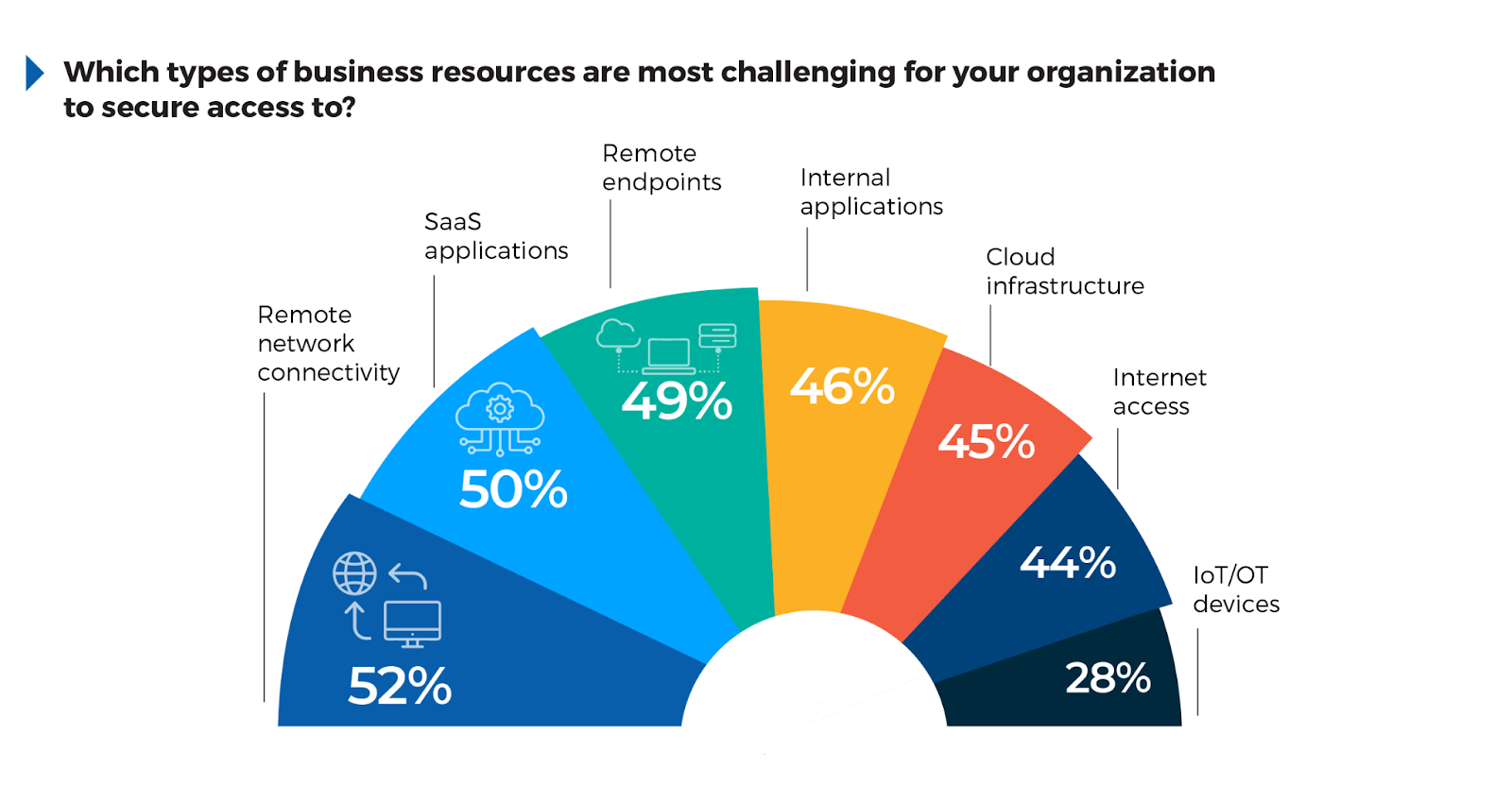
As organizations continue to adopt cloud services and remote work, securing access to essential business resources has become one of the most pressing cybersecurity challenges. The survey asked which resources are most difficult to secure, underscoring the complexities of managing distributed infrastructures while maintaining consistent security.
The results show that 52% of respondents find remote network connectivity (e.g., VPNs) to be the most challenging to secure. This reflects the inadequacies of legacy VPNs in handling scalable and secure connections for dispersed teams as the backhauling of traffic to remote data centers introduces high latency and reduced performance, along with significant security vulnerabilities.
50% cited SaaS applications like Microsoft 365, highlighting the difficulty of enforcing data governance and access control across cloud-based services. Similarly, 49% noted the challenge of securing remote endpoints (e.g., laptops, mobile devices), emphasizing the risks associated with unmanaged devices operating outside of controlled environments.
Additionally, securing internal applications (46%) and cloud infrastructure (45%) remains complex as companies adopt hybrid cloud environments where security policies must span multiple platforms. To address these challenges, organizations should consider using flexible, scalable platforms that unify security across remote networks, SaaS, and endpoint devices. SASE platforms help eliminate the need for traditional VPNs, providing secure, direct access to cloud and on-prem applications through SDWAN and ZTNA, without compromising performance.
Managing Secure Access: Complexity and Visibility Gaps
As organizations scale their operations and embrace a mix of cloud, on-premises, and remote infrastructures, managing secure access has become more challenging.
The most pressing issue, reported by 23% of respondents, is the complexity of managing access policies across multiple platforms. This highlights the strain organizations face when trying to maintain consistency across fragmented systems. Similarly, 16% cited rising costs related to scaling capacity and bandwidth. Lack of visibility into user activity (14%) is another critical issue, as gaps in monitoring can leave organizations vulnerable to undetected threats, especially as cloud use grows.
Additional challenges include inflexible technologies that struggle to support mixed environments (11%) and excessive user privileges (10%), both of which can expose organizations to risks. Less frequently mentioned but still relevant concerns, like latency and integration issues, signal the persistent technical difficulties organizations face with legacy systems.
To address these challenges, organizations should turn to integrated platforms like SSE, which streamline policy enforcement across various environments and provide real-time visibility into user activities. Investing in cloud-native solutions with built-in scalability and adopting Zero Trust principles can significantly reduce complexity, ensuring security controls evolve alongside business needs. Additionally, focusing on technologies that provide granular user access control can help prevent privilege misuse while maintaining flexibility in policy enforcement.

Filling Strategic Gaps with MSSPs
The inherent challenges of cybersecurity threats and the rapid evolution of attack methods have left many organizations struggling to maintain sufficient in-house defense capabilities. This challenge drives the need for strategic partnerships with MSSPs, enabling companies to fill critical skill gaps and access advanced security solutions that would otherwise be beyond their internal capacity.
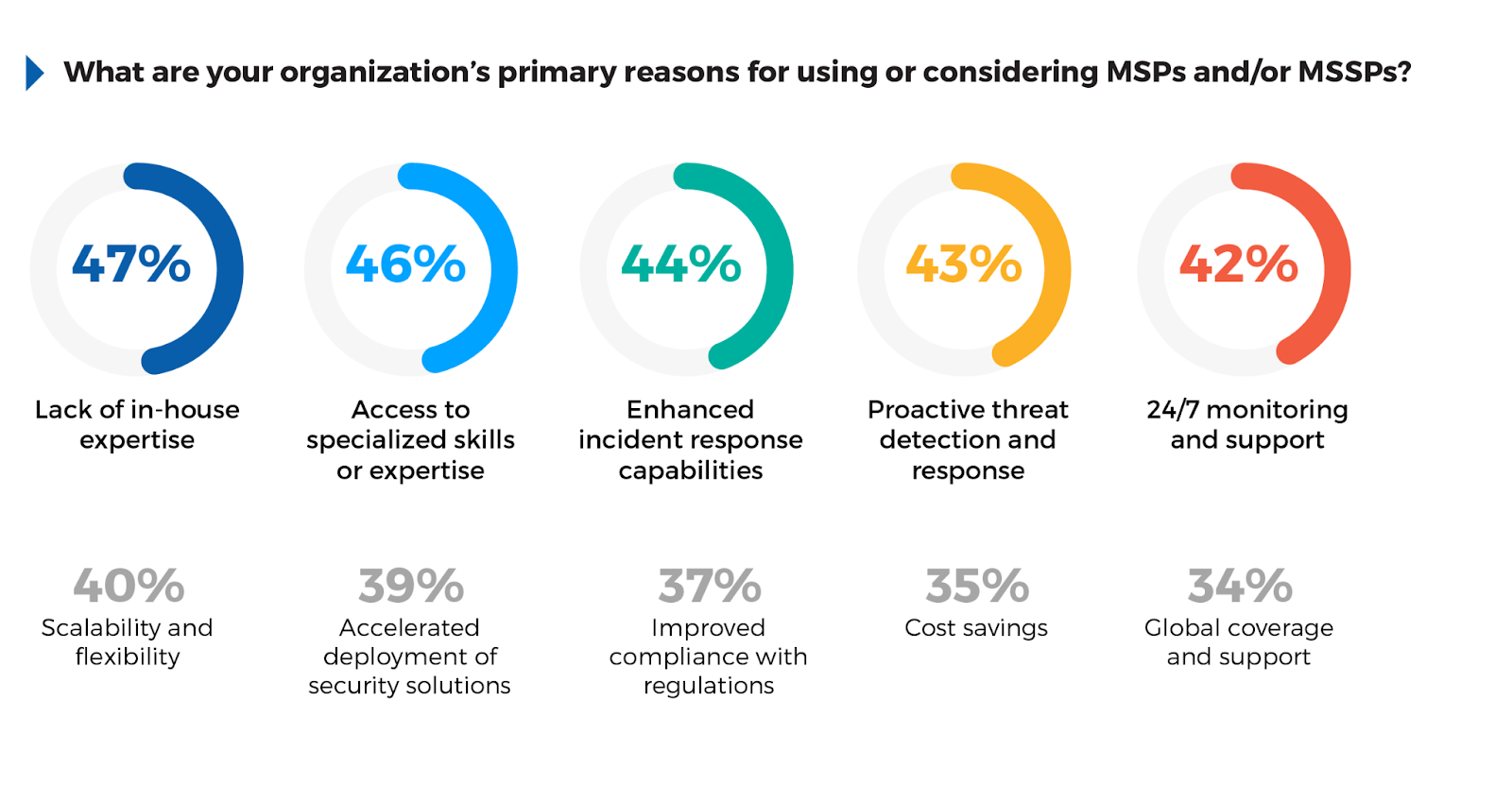
The survey shows that 47% of respondents identified lack of in-house expertise as a key reason for turning to MSSPs. This highlights a common issue: many organizations, despite their investment in cybersecurity, lack the deep, specialized skills needed to manage complex security tasks at scale.
In response, 46% of participants seek external access to specialized skills or expertise, recognizing that third-party providers can offer capabilities such as advanced threat detection and response that would be costly or impractical to build internally. Enhanced incident response capabilities (44%) and proactive threat detection (43%) were frequently cited, reflecting the importance of having robust, responsive measures in place to mitigate sophisticated attacks.
For security teams, leveraging MSSPs can provide much-needed flexibility and scale, enabling a stronger defense without overwhelming internal resources. However, organizations should look for providers that integrate seamlessly with their existing security architecture, offering proactive services such as threat intelligence and automated incident response. By doing so, they can enhance their security posture while maintaining agility and focusing on strategic initiatives.
Growing SASE Adoption and Urgency
As digital transformation accelerates and IT environments evolve, the need for a unified, cloud-centric approach to secure network access has intensified.
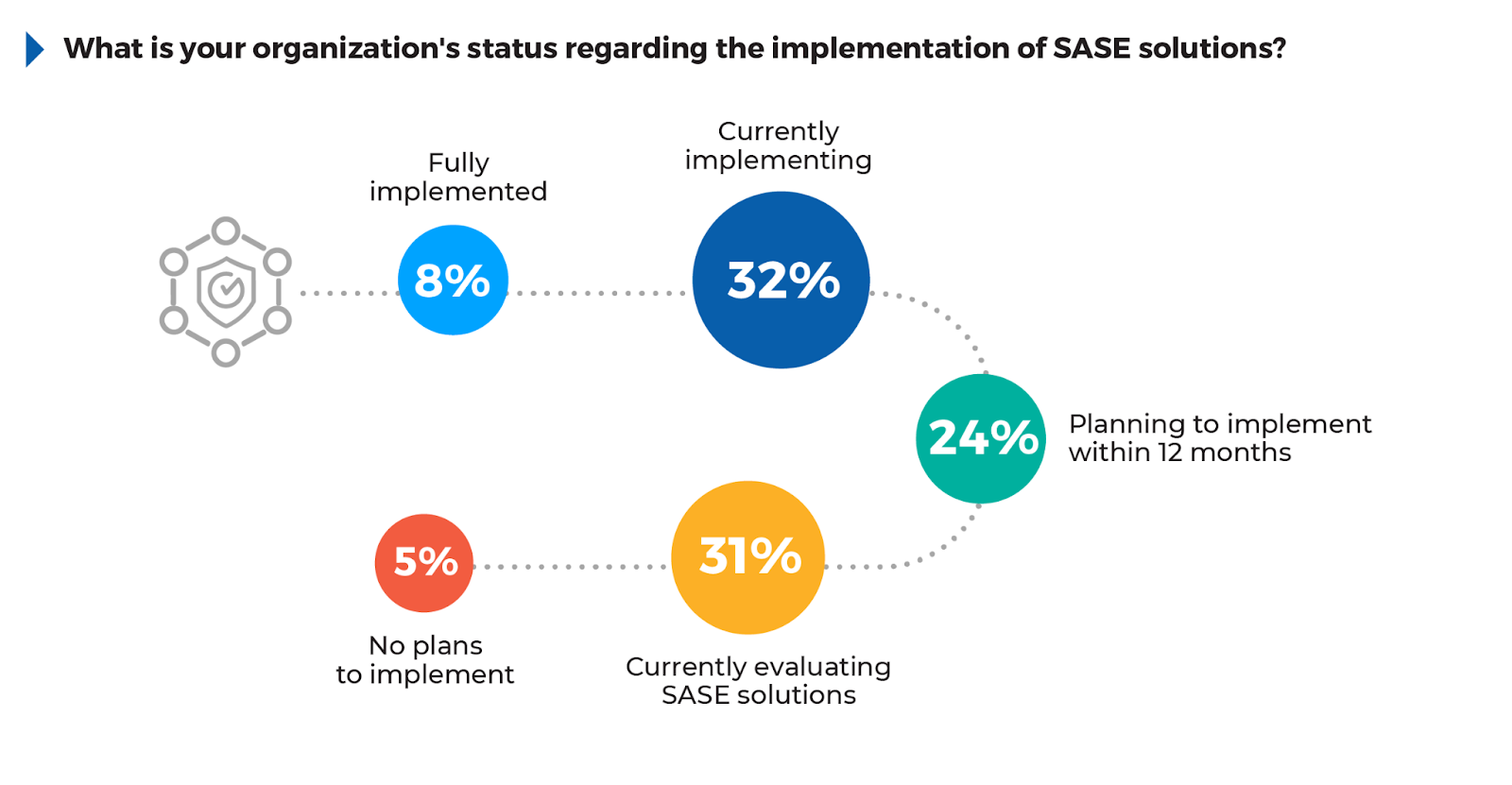
According to the survey, 32% of respondents are currently implementing SASE solutions, reflecting the growing momentum toward adopting this architecture. An additional 31% are currently evaluating SASE solutions. Combined with those planning to implement within the next year (24%), it’s critical that these organizations prioritize SASE solutions quickly in order to maintain security.
Despite strong interest, only 8% of organizations have fully implemented SASE, highlighting the complexity and gradual nature of this transition. This slow progress leaves organizations vulnerable as threat actors accelerate their tactics, striking with unprecedented speed and sophistication.
Given the growing adoption rate, organizations should focus on integrating SASE components, prioritizing technologies like ZTNA, SWG and Cloud Security Access Brokers (CASB) that provide immediate security benefits for cloud and remote work environments. Partnering with managed service providers that specialize in SASE deployment can further accelerate the process and help overcome integration challenges, allowing businesses to leverage the scalability, flexibility, and comprehensive security capabilities that SASE offers.
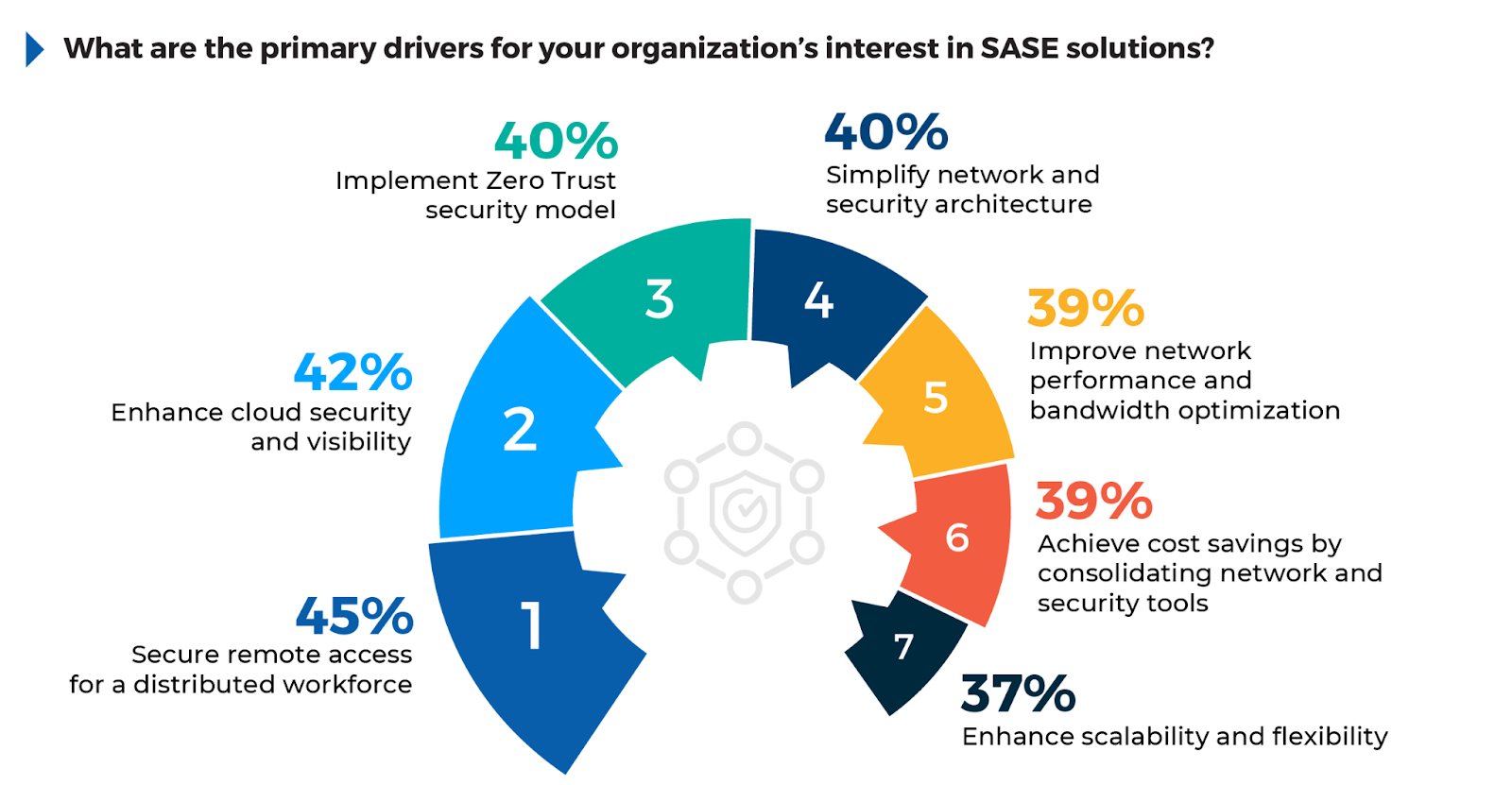
The Drivers Behind SASE Adoption
The survey reveals key factors driving the adoption of SASE solutions, which continue to gain traction as organizations modernize their security and networking infrastructures. 45% of respondents point to secure remote access for a distributed workforce as the leading driver, highlighting the ongoing need to safeguard access for remote and hybrid workers.
42% of respondents cite the need to enhance cloud security and visibility, showing that as businesses migrate to the cloud, maintaining control over data and securing access points remain significant challenges. Meanwhile, 40% express a desire to implement a Zero Trust security model and simplify their network and security architecture, indicating that organizations want to consolidate complex infrastructures and adopt continuous verification principles. Other notable factors include improving network performance (39%) and achieving cost savings through consolidation of tools (38%).
To capitalize on these drivers, organizations should focus on deploying SASE platforms that integrate Zero Trust principles with unified security across cloud and remote environments. By enhancing visibility and optimizing network performance, SASE offers a comprehensive approach that simplifies operations and strengthens security, making it essential for companies undergoing digital transformation.
Benefits Driving SASE Adoption
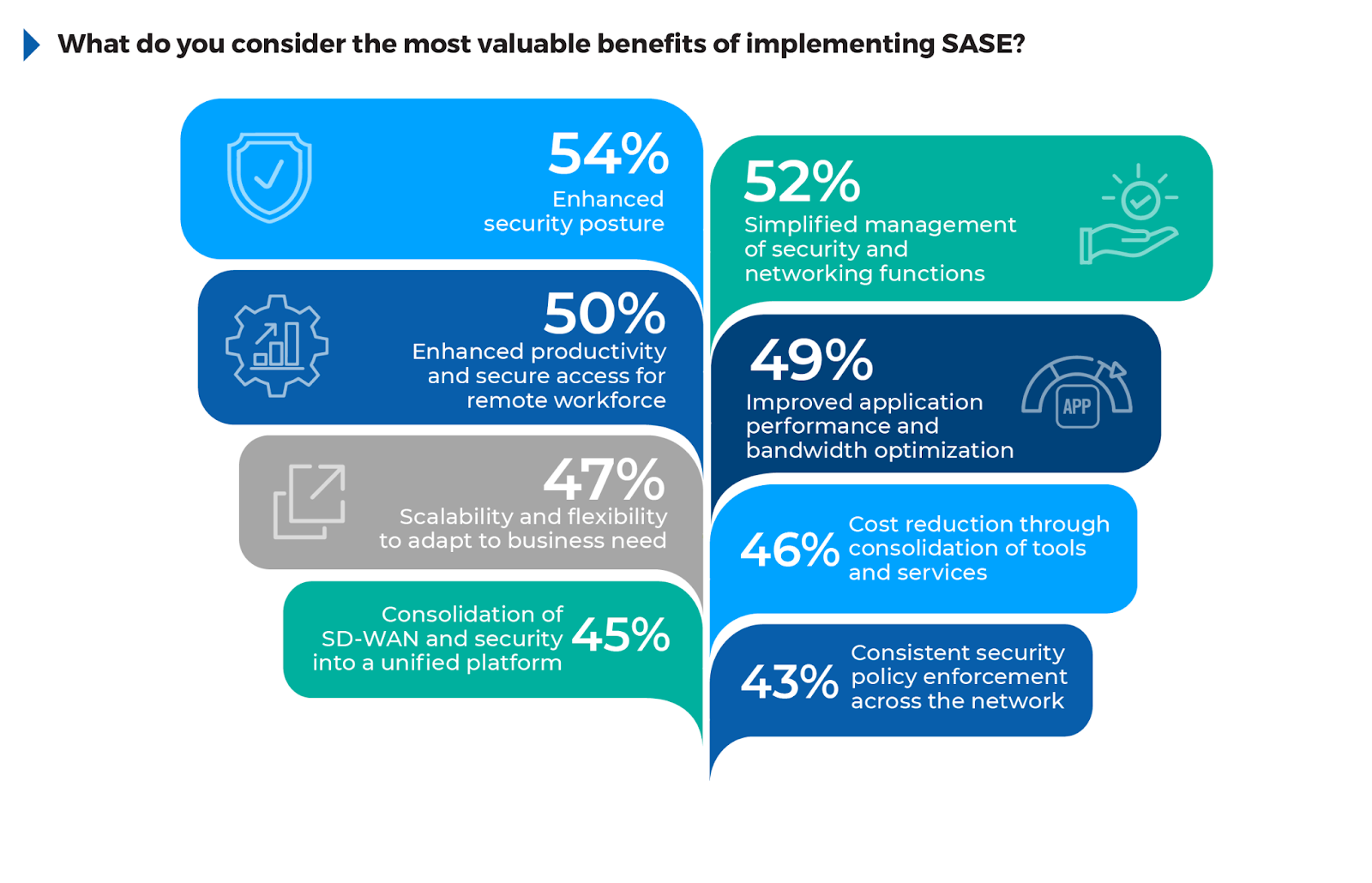
The survey results reveal a clear set of priorities driving organizations to adopt SASE solutions, reflecting the wide-ranging benefits that this architecture brings to both security and network management.
54% of respondents report an enhanced security posture, showing that organizations prioritize SASE’s ability to integrate security directly into the network, thereby reducing vulnerabilities. 52% value the simplified management of security and networking functions, reflecting SASE’s consolidation of tools and reduced complexity in managing hybrid infrastructures.
50% of respondents noted enhanced productivity and secure access for remote workforces as key benefits, underscoring the importance of seamless, secure access for distributed teams. Improved application performance and bandwidth optimization was highlighted by 49%, pointing to SASE’s ability to use SD-WAN for intelligent traffic routing.
Organizations can fully leverage these benefits by prioritizing SASE deployments that unify network and security functions, enhancing scalability and reducing operational overhead. This approach not only strengthens security but also supports productivity and optimizes network performance, aligning with broader digital transformation efforts.
Key Challenges in Implementing SASE
Organizations adopting SASE face a variety of challenges, especially as they attempt to integrate these solutions into their existing infrastructure. 48% of respondents identified integration with existing systems as their biggest challenge, underscoring the difficulty in aligning legacy infrastructure with modern, cloud-native architectures. 44% also reported struggles with policy management across multiple environments, reflecting the challenge of ensuring consistent security controls across on premises, cloud, and remote work settings.
Operational and transitional issues are also significant, with 38% concerned about user disruption during transition and 37% struggling to phase out legacy security tools. These challenges are further compounded by a lack of in-house expertise (37%), as many organizations don’t have the skill sets needed to effectively manage SASE deployments at scale.
To mitigate these issues, organizations should focus on identifying specific integration points where SASE can provide immediate value, such as enhancing cloud security visibility or improving remote access management. Partnering with SASE providers that offer built-in integration, APIs, and automation features can reduce the burden of policy management and limit downtime.

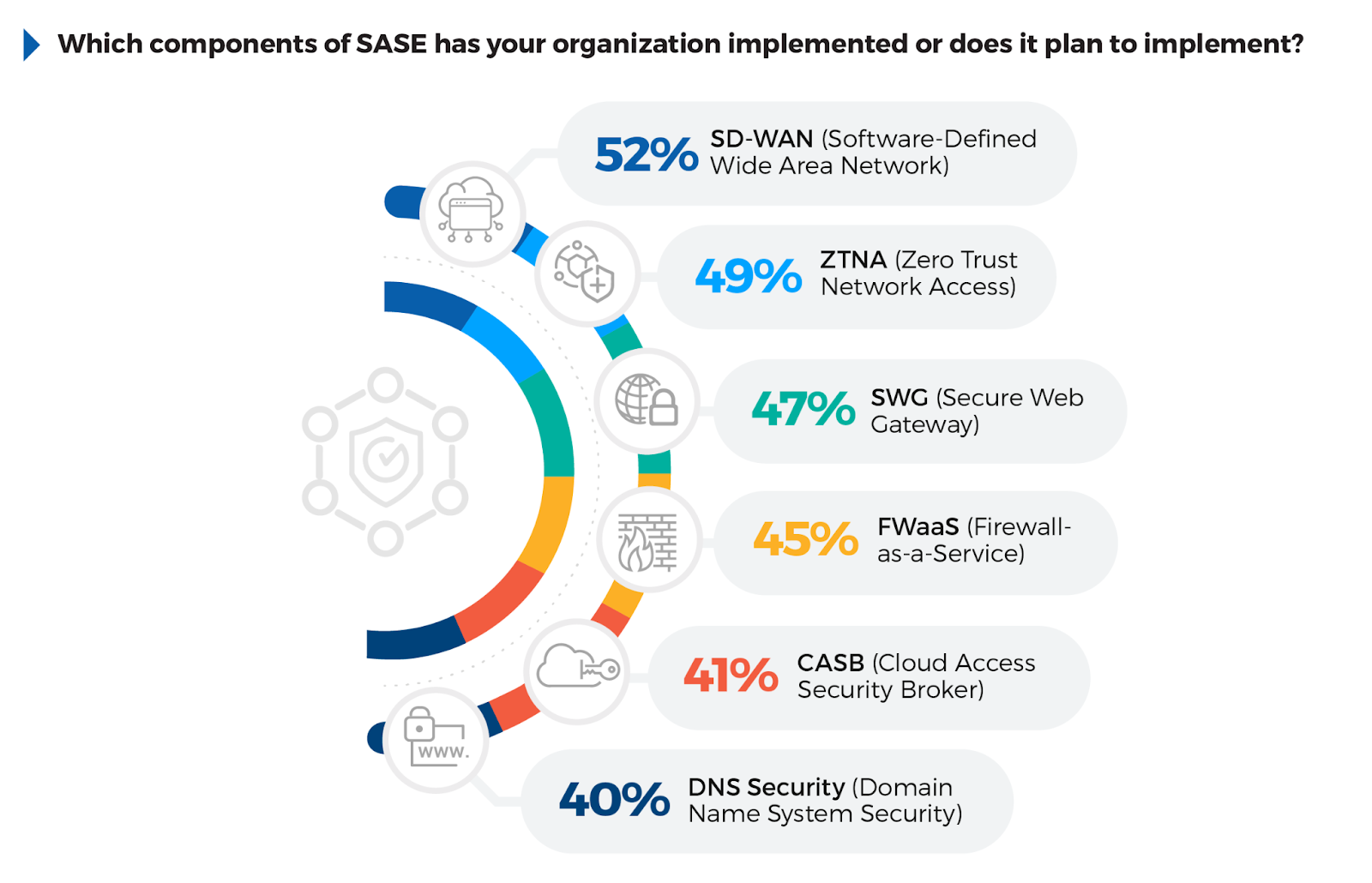
SASE Components Adoption
Understanding which components of SASE organizations are prioritizing offers valuable insight into how they are modernizing their security strategies. The key component, SD-WAN has been implemented or planned by 52% of respondents, highlighting its role in optimizing network performance for distributed environments. ZTNA follows closely at 49%, reflecting the importance of Zero Trust principles in securing remote access. 47% have adopted SWG, emphasizing the need for securing web traffic and enforcing policies.
FWaaS at 45% reflects a clear shift towards cloud-delivered security, while CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) at 41% underscores the need for securing cloud applications more robustly.
To succeed in SASE implementation, organizations should focus on deploying high-impact components like SD-WAN and ZTNA first. Simplifying management by consolidating these services into integrated platforms will reduce complexity and improve scalability. Partnering with managed service providers that offer seamless integration can help ease the transition while ensuring ongoing optimization.
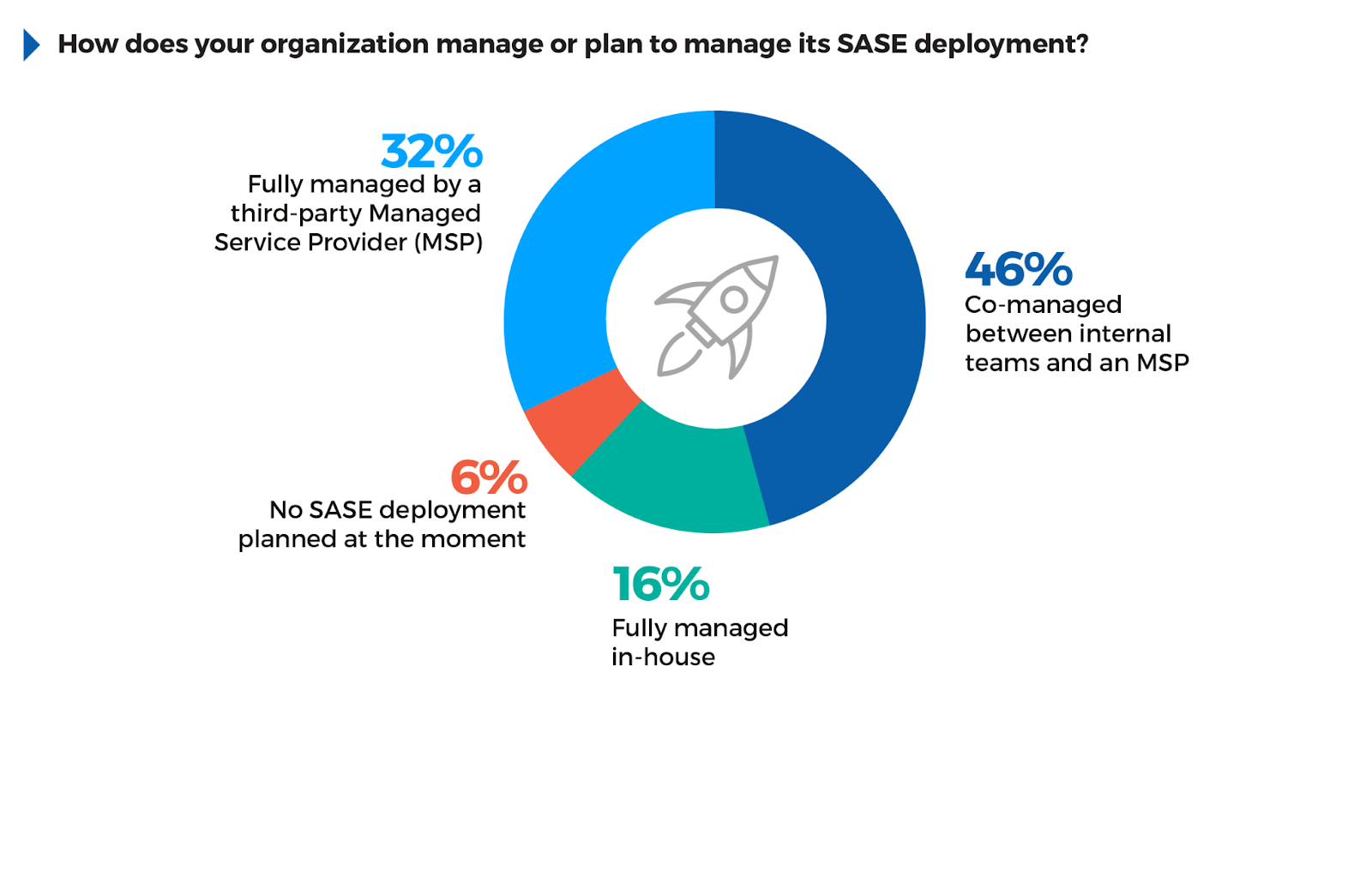
SASE Management Models
The decision of how to manage an SASE deployment often reflects an organization’s need to balance control with complexity and availability of skilled resources. 46% of respondents favor a co-managed approach with an MSP, indicating a common strategy of retaining oversight while leveraging external expertise for operational management. This model helps bridge internal capability gaps without fully relinquishing control over the infrastructure.
Meanwhile, 32% opt for fully managed SASE by an MSP, suggesting that many organizations prefer outsourcing to simplify their SASE deployment and management, especially those with limited resources. 16% manage SASE in-house, likely representing larger organizations with strong internal IT and security expertise.
Organizations should align their management model with their overall security strategy and internal resources. A co-managed approach provides flexibility, while outsourcing to MSPs ensures technical expertise and scalability, especially when internal teams are limited.
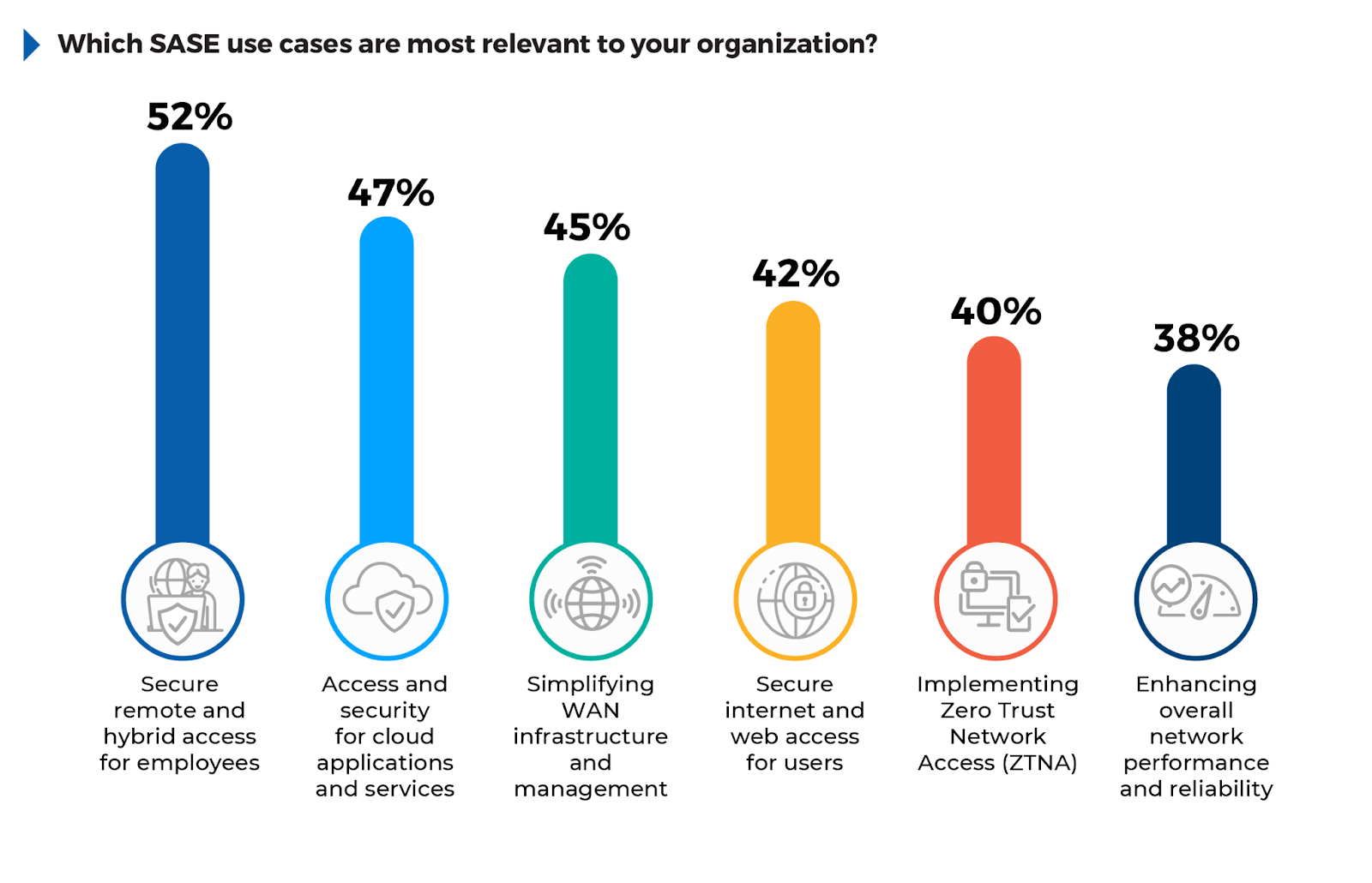
Key SASE Use Cases for Organizations
Understanding the most relevant use cases for SASE can help organizations prioritize deployment strategies based on their unique networking and security needs.
According to the survey, 52% of respondents consider secure remote and hybrid access for employees the most relevant use case, driven by the need to protect distributed workforces and access scenarios. Access and security for cloud applications ranked next at 47%, reflecting the increasing reliance on SaaS platforms and the growing importance of cloud security. Simplifying WAN infrastructure and management (45%) highlights the push to streamline network operations as organizations transition to SD-WAN.
Other key use cases include secure internet access (42%) and ZTNA (40%), both of which focus on securing user traffic and identities across network environments.
To fully leverage these use cases, organizations should deploy SASE solutions that address secure access for remote work, cloud services, and WAN management, ensuring seamless security and consistent policy enforcement across all IT environments.
SASE and SSE: Distinct Roles in Unified Security
Many cybersecurity professionals wonder how SASE and SSE differ, as both play critical roles in securing today’s complex, distributed environments.
SASE and SSE share common goals in modern cybersecurity architectures but differ in scope and focus. Both aim to unify and simplify security for distributed networks, yet while SASE encompasses networking and security functions, SSE focuses solely on the security side.
SASE
Combines security with network optimization by integrating technologies such as SDWAN and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) with Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Firewallas-a-Service (FWaaS), and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) within a single, cloudnative framework. This approach enables organizations to secure remote access while ensuring optimal network performance.
SSE
As a subset of SASE, narrows the focus to security controls—specifically SWG, CASB, and ZTNA—without incorporating networking aspects like SD-WAN. SSE is ideal for organizations prioritizing security and access control, often working in tandem with existing network solutions.
In essence, SASE is suited for organizations needing a unified, end-to-end network and security approach, while SSE serves those focused on strengthening security postures in existing network frameworks. Both models help enforce Zero Trust principles and offer centralized management, enhancing scalability and control in cloud-centric, distributed environments.
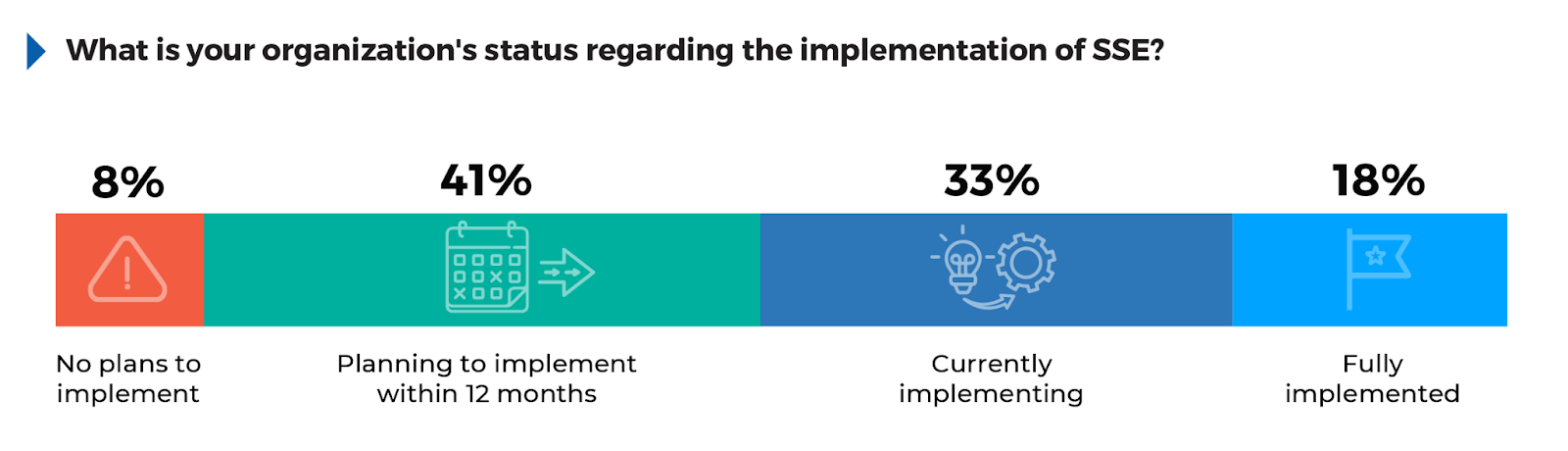
SSE Adoption: A Path to Enhanced Security
Understanding the adoption of SSE offers insight into how organizations are securing cloud access and enforcing consistent security policies across increasingly distributed environments.
According to the survey, 41% of respondents are planning to implement SSE within 12 months, showing that many organizations are still in the evaluation or preparation phase. This suggests that while interest in SSE is high, full deployment remains a future priority for many. 33% are currently implementing SSE, indicating that a significant portion of organizations are actively transitioning to this model. Meanwhile, 18% have fully implemented SSE, reflecting that while adoption is underway, few have reached full maturity. Only 8% of respondents report having no plans to implement SSE, likely because they either have alternative solutions in place or are not yet ready to transition to cloud native security.
To accelerate SSE adoption, organizations should consider focusing on specific pain points, such as improving cloud security and ensuring visibility across hybrid work environments. A targeted approach that addresses immediate needs, such as securing remote access or optimizing application performance, can deliver quick wins and drive faster overall implementation. Additionally, aligning SSE deployment with existing business initiatives, like cloud migration or Zero Trust strategies, ensures that the transition integrates smoothly with ongoing projects without overwhelming internal teams.
Key Drivers for SSE Adoption
Identifying the primary reasons organizations are adopting SSE reveals the strategic benefits driving its implementation.
The survey shows that 55% of respondents prioritize enhanced cloud security and visibility as the top driver, reflecting the need to protect cloud environments where traditional security tools fall short. 48% are motivated by implementing Zero Trust strategies, emphasizing the importance of reducing insider threats and improving access control. Simplifying remote access for distributed workforces (45%) highlights the ongoing demand for secure, efficient access solutions.
Additional drivers include simplifying security management (44%) and enhancing scalability (39%), showing the need for flexible solutions that can grow with the business. Improving network performance (37%) and meeting compliance requirements (35%) also rank high, indicating SSE’s ability to reduce latency and enforce consistent security policies.
To address these drivers, organizations should focus on deploying SSE solutions that tackle their most immediate needs first, such as real-time data protection, cloud security, and efficient remote access.

SASE: Optimizing Secure Network Access
As digital transformation accelerates and IT landscapes evolve, the need for a unified, cloud-centric approach to secure network access has intensified. SASE, or Secure Access Service Edge, combines networking and security into a single, cloud-native framework, providing a comprehensive solution that addresses the needs of remote work, cloud migration, and increasingly distributed workforces.
What SASE Offers
SASE architectures bring together essential technologies—such as SD-WAN, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS)—into a cohesive security model designed to operate seamlessly across both cloud and on-premises environments. With strategically placed global points of presence (PoPs), SASE enables consistent and high-performance access to cloud resources and applications by minimizing latency and optimizing traffic flow.
Why SASE Matters
The traditional network security model, focused on perimeter defense, has been disrupted by the growth of hybrid workforces (implemented by 63% of organizations) and the adoption of cloud services. With SASE, remote users gain direct, secure access to applications and data without the need for inefficient traffic backhauling, allowing organizations to maintain control and enforce security policies wherever users and applications are located. Using a unified, cloud-based security infrastructure, SASE simplifies network management and reduces operational complexity by consolidating tools and eliminating redundant infrastructure.
SASE Benefits
1. Performance Optimization: SASE enhances application and network performance by routing traffic through distributed points of presence (PoPs), strategically located data centers, or nodes distributed globally. These PoPs act as on-ramps to cloud services, ensuring minimal latency and maximum efficiency, particularly for remote workers, regardless of their location.
2. Simplified Management: By converging security and networking in a single platform, SASE enables centralized policy control, visibility, and reporting across all environments.
3. Enhanced Security Posture: Integrating technologies like ZTNA, SWG, and CASB into the network enables real-time threat detection and response, ensuring that only trusted users can access sensitive resources.
4. Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud-based delivery provides elastic scalability, which adapts seamlessly to fluctuating bandwidth needs and offers resilience for expanding cloud environments.
5. Reduced Operational Burden: With a managed SASE approach, organizations can offload significant operational demands, focusing internal resources on strategic objectives rather than routine security management.
For organizations facing evolving network demands, SASE offers an adaptable, unified framework that bridges the gap between security and networking while optimizing access to cloud applications and internet services. This approach empowers security teams to enforce Zero Trust principles and simplifies the management of complex, distributed environments.
Next Steps: Best Practices for Secure Network Access
Securing network access across hybrid and cloud environments requires adopting an integrated, multifaceted technology strategy. The following best practices offer a streamlined approach to strengthen security while reducing complexity.
1.DEPLOY SASE FOR UNIFIED SECURITY
With 52% of organizations finding remote network connectivity challenging, SASE integrates key components like SD-WAN and ZTNA to secure remote and hybrid access. Focus on these core components to streamline operations while enhancing security.
2.SIMPLIFY POLICY MANAGEMENT
Managing access policies across multiple environments is a key issue for organizations. Simplify this process with platforms like SASE or SSE, which provide centralized management and realtime visibility.
3.ADOPT A ZERO TRUST SECURITY STRATEGY
Zero Trust continuously verifies users and devices, ensuring secure access. With 42% of organizations planning to implement Zero Trust soon, focus on implementing ZTNA to protect against unauthorized access.
4.ENHANCE CLOUD SECURITY
55% of respondents cited cloud security and visibility as a major driver for SSE. Tools like CASB enforce governance and protection for cloud apps, ensuring data security in distributed work environments.
5.INVEST IN SCALABILITY AND FLEXIBILITY
39% of respondents highlight the need for scalable security solutions. Cloud-based platforms such as SASE offer flexible, scalable security that adapts to growing infrastructures, improving both performance and security.
6.FOCUS ON COMPLIANCE
Meeting compliance needs is critical for 35% of organizations. Integrated platforms like SSE provide built-in compliance controls, helping align security with industry regulations and streamlining audits.
7.LEVERAGE MANAGED SECURITY SERVICES
47% of respondents rely on managed services due to in-house skill gaps. By partnering with MSSPs, organizations can benefit from SASE / SSE expertise, continuous monitoring, and expert threat detection, without overburdening internal teams.
These best practices help organizations address security challenges while supporting flexibility, scalability, and control across hybrid and cloud environments.
Conclusion
As organizations continue to adapt to the demands of increasingly distributed IT environments and heightened security challenges, the findings of this report underscore the critical importance of modern, integrated approaches such as SASE and SSE.
While interest and adoption rates are rising, the complexities of full implementation remain a hurdle. Strategic investments in scalable, cloud-native solutions, along with partnerships that bridge expertise gaps, will be essential in maintaining robust security postures.
By prioritizing flexible architectures and embracing Zero Trust principles, organizations can better position themselves to face evolving threats and ensure secure, seamless access across all environments.
Methodology and Demographics
This 2025 Secure Network Access Report is based on a comprehensive online survey of 411 cybersecurity professionals, conducted in November 2024, to gain deep insight into the latest trends, key challenges, and solutions for secure network access.
The survey utilized a methodology ensuring a diverse representation of respondents, from technical executives to IT security practitioners, across various industries and organization sizes. This approach ensures a holistic and balanced view of the network security landscape, capturing insights from different organizational perspectives.
__
About Hughes
Hughes Network Systems provides broadband equipment and services; managed services featuring smart, software-defined networking; and end-to-end network operation for millions of consumers, businesses, and governments worldwide.
As a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP), we provide customers with comprehensive security coverage that protects, detects, and responds to modern threats. With an extensive networking background, Hughes Managed Cybersecurity Services provides businesses of all sizes with the convergence of network and security solutions they desire. Top brands in the restaurant, retail, franchise, grocery, c-store & retail petroleum, government, and healthcare industries rely on Hughes for managed network services. Our experience managing large networks gives us a unique advantage when it comes to cybersecurity. We know how to defend networks because we’ve been building customer networks for decades. Customers rely on our proven experience, leading innovation, and top tier customer service delivery.
There is a strong amount of synergy between our services, which include Managed SASE, Managed Detection and Response (MDR), Network Detection and Response (NDR), Ransomware & Zero-Day Prevention, and Unified Threat Management (UTM). Our customers also take advantage of our Managed Network Services, such as Wi-Fi, VoIP, Wireless 5G, Managed LEO, Digital Signage, and more.
Learn how Hughes Managed Cybersecurity can protect your business. Learn more www.hughes.com
__
Cybersecurity Insiders brings together 600,000+ IT security professionals and world-class technology vendors to facilitate smart problem-solving and collaboration in tackling today’s most critical cybersecurity challenges.
Our approach focuses on creating and curating unique content that educates and informs cybersecurity professionals about the latest cybersecurity trends, solutions, and best practices. From comprehensive research studies and unbiased product reviews to practical e-guides, engaging webinars, and educational articles – we are committed to providing resources that provide evidence-based answers to today’s complex cybersecurity challenges.
For more information: email us info@cybersecurity-insiders.com or visit cybersecurity-insiders.com
The post State of Secure Network Access 2025 appeared first on Cybersecurity Insiders.
February 20, 2025 at 05:30PM










