Key Insights and Strategies for Protecting Cloud Environments
Introduction
Cloud adoption is continuing to transform the IT infrastructure and security landscapes by delivering unmatched scalability and flexibility. Multi-cloud strategies further enhance these advantages but introduce unique challenges, prompting organizations to implement innovative solutions to safeguard their critical assets effectively.
The 2025 State of Cloud Security Report, based on insights from 873 cybersecurity professionals, provides an in-depth analysis of the evolving cloud security landscape, highlighting key trends, challenges, and priorities for organizations navigating increasingly complex environments. This report serves as a guide for IT and security professionals seeking to strengthen their hybrid and multi-cloud security posture while continuing innovation.
Key findings from this report include:
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies on the Rise: Over 78% of respondents utilize two or more cloud providers, underscoring the growing importance of multi-cloud approaches to enhance resilience and leverage specialized capabilities. 54% of organizations have adopted hybrid cloud models, integrating on-prem and public cloud environments to optimize flexibility and control.
- Security and Compliance Top Concerns: Security and compliance issues are the primary barriers to cloud adoption, cited by 61% of organizations striving to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive data.
- Skills Gap in Cloud Security Expertise: 76% of organizations report a shortage of expertise in cloud security, highlighting the need for automation, targeted upskilling, and resource optimization.
- Low Confidence in Real-Time Threat Detection: The survey data highlights that 64% of respondents lack confidence in their organization’s ability to handle real-time threat detection.
- Unified Cloud Security Platforms: The survey shows 97% of respondents prefer unified cloud security platforms with centralized dashboards to simplify policy configuration, ensure consistency, and enhance visibility across an organization’s cloud footprint.
- Rapid Adoption of Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP): To address misconfigurations and compliance gaps, 67% of respondents are implementing CSPM and 62% CNAPP solutions to protect cloud environments.
This report underscores the importance of unified cloud security solutions that streamline policy enforcement, automate threat detection, and ensure consistent protection across hybrid and multicloud environments. By leveraging these insights and best practices, organizations can build a resilient cloud security posture that adapts to evolving threats and business demands.
We extend our sincere gratitude to Fortinet, a global leader in cloud security, for their invaluable contribution to this research. Their expertise and insights into securing hybrid and multi-cloud environments have significantly strengthened the findings and recommendations presented in this report.
We hope this report serves as a valuable resource for IT and cybersecurity professionals striving to secure their organizations in this era of rapid cloud expansion.
Thank you,
Holger Schulze Founder
Cybersecurity Insiders
Shifting Cloud Deployment Strategies
The choice of an organization’s cloud deployment strategy directly impacts its security needs, operational outcomes, and infrastructure requirements, making it a pivotal decision in today’s multi-faceted IT environments.
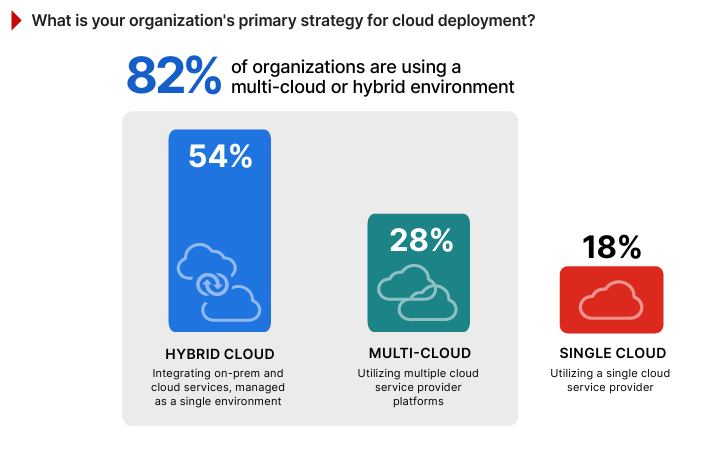
The survey findings show that hybrid cloud is the predominant strategy, chosen by 54% of respondents, up from 43% last year. This growth reflects a strong shift away from single-cloud toward integrating multiple cloud services with on-premises systems into cohesive environments. For example, a retail company might use a public cloud to host customer-facing applications while retaining sensitive payment data in a private on-premises system to meet compliance requirements like PCI DSS. Such hybrid strategies allow organizations to enjoy the scalability of public clouds while maintaining control over critical data.
Multi-cloud deployments, which are critical for scenarios where organizations distribute workloads across providers to avoid vendor lock-in or utilize specific capabilities, follow at 28%. For instance, a tech company might host its compute-heavy applications on Amazon Web Services (AWS) while using Google Cloud’s advanced AI services for data analytics, ensuring they optimize performance while mitigating reliance on a single provider.
Single cloud adoption is becoming less common, with just 18% relying on a single provider (down from 22% in 2024), often reflecting simplicity in management at the potential cost of reduced flexibility. This may be the preferred model for smaller businesses, such as a law firm exclusively using Microsoft’s Azure for its document storage and workflow management, prioritizing ease of management over diversification.
Expanding Multi-Cloud Adoption
The increasing number of cloud providers that organizations use reflects the evolving preference for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, as well as the operational complexity they introduce.
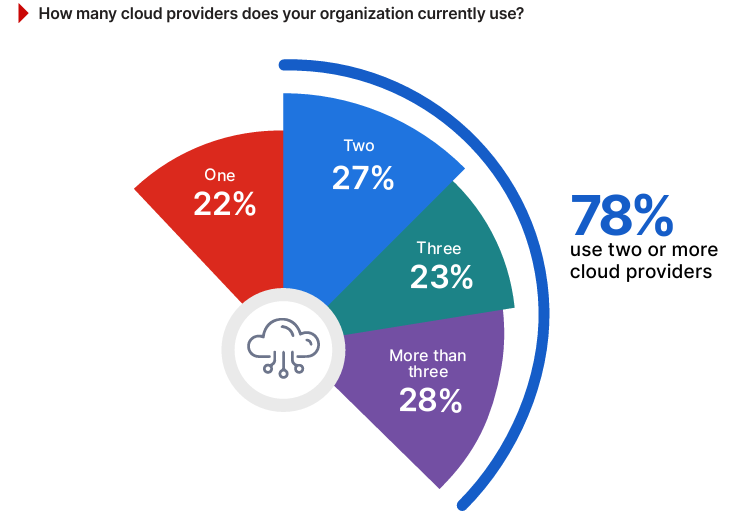
The survey results reveal that 78% of organizations use two or more cloud providers, up from 71% last year, marking a 7-point increase that underscores the growing shift toward multi-cloud adoption. For example, a multinational company might use AWS for its global content delivery network while relying on Microsoft Azure’s compliance-ready offerings in regions with strict data residency laws. The strategic use of multiple providers enables businesses to leverage specialized capabilities, such as AI services from Google Cloud or Oracle Cloud’s database expertise, while ensuring resilience through redundancy.
Dominance of Major Cloud Providers
Understanding which cloud service providers organizations currently use, or plan to adopt, sheds light on market preferences and reveals how businesses align their cloud strategies with evolving workloads and specialized capabilities.
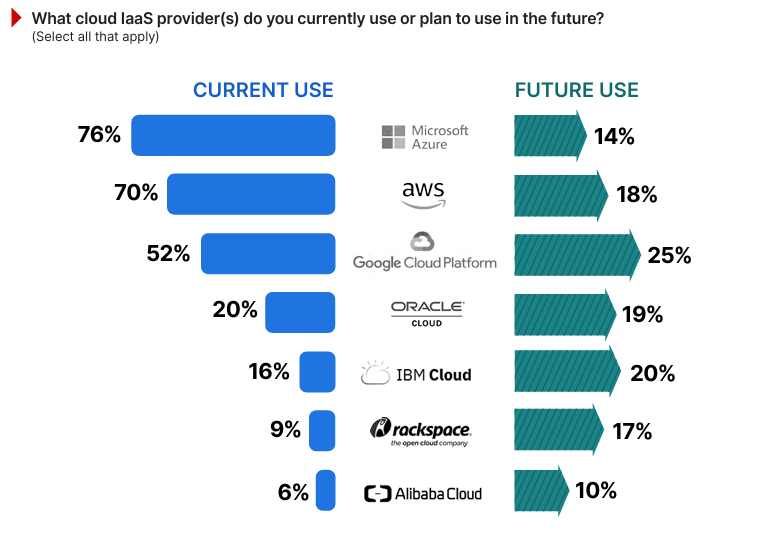
The findings confirm Microsoft Azure and AWS as dominant players, with 76% and 70% of respondents reporting current usage, respectively.
Currently used by 52% of respondents, the Google Cloud Platform is gaining interest, as reflected by 25% of respondents planning to adopt it in the future.
Meanwhile, Oracle Cloud and IBM Cloud maintain smaller market shares but see notable future interest, likely driven by their expertise in integrating with enterprise legacy systems.
Overcoming Barriers to Cloud Adoption
The survey reveals the primary barriers organizations face in adopting cloud services, highlighting the challenges IT and security teams must address to fully realize the potential of cloud environments.
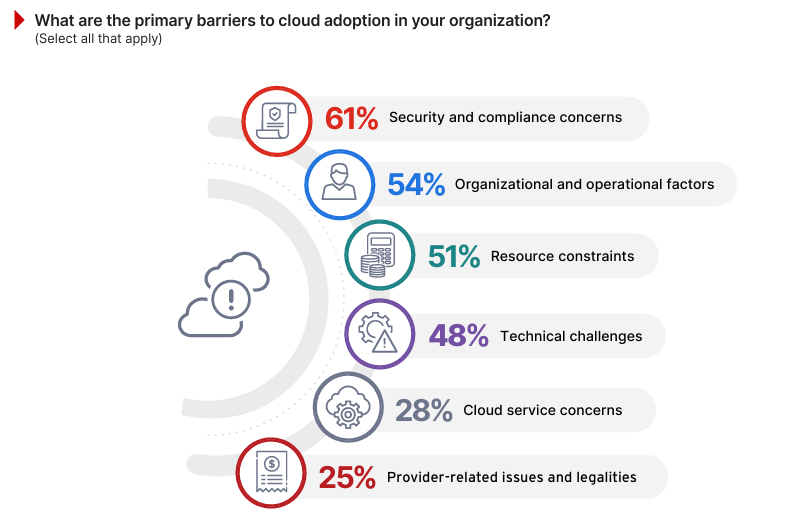
Security and compliance concerns remain the top challenge, cited by 61% of respondents (up from 59% in last year’s survey). This reflects growing interest around issues like data leakage and the complexities of meeting regulatory requirements. For instance, a healthcare organization might delay migrating sensitive patient records to the cloud due to uncertainty around compliance with HIPAA or other regional data protection laws.
Organizational and operational factors follow closely at 54% (moving up to #2 spot from 49% last year), highlighting challenges such as resistance to change, vendor lock-in concerns, and cultural hurdles. A manufacturing company, for example, may face internal pushback when moving legacy systems to the cloud due to fears of losing control over proprietary processes.
Resource constraints, including limited staff expertise and budgetary restrictions, are cited by 51% (up from 49% in 2024), emphasizing the difficulty many organizations face in managing and securing cloud capabilities. Meanwhile, technical challenges, though slightly less prominent this year at 48%, still represent a substantial barrier, particularly when integrating complex hybrid cloud environments.
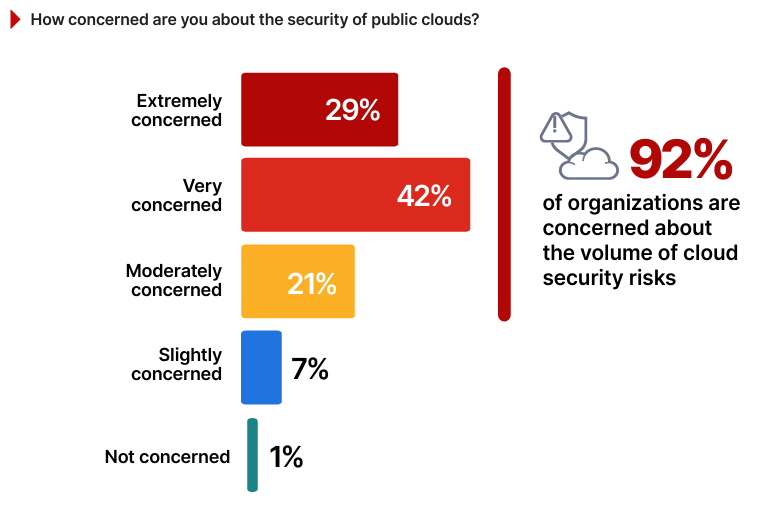
Public Cloud Security Concerns
Persistent concerns about the security of public clouds reflect the ongoing challenge of balancing the benefits of scalability and agility with the need for robust protection.
A staggering 92% of survey respondents expressed concern about public cloud security, underscoring its importance as a critical area of focus for IT and cybersecurity professionals.
This apprehension aligns with findings in this survey where 61% identified security and compliance as the top barrier to cloud adoption. For example, a financial services firm considering cloud migration for customer transaction data might hesitate due to fears of regulatory non-compliance or potential exposure of sensitive information through misconfigurations. Such concerns extend to specific risks, including data leakage, shared responsibility confusion, and limited visibility into cloud provider activities, further complicating adoption decisions.
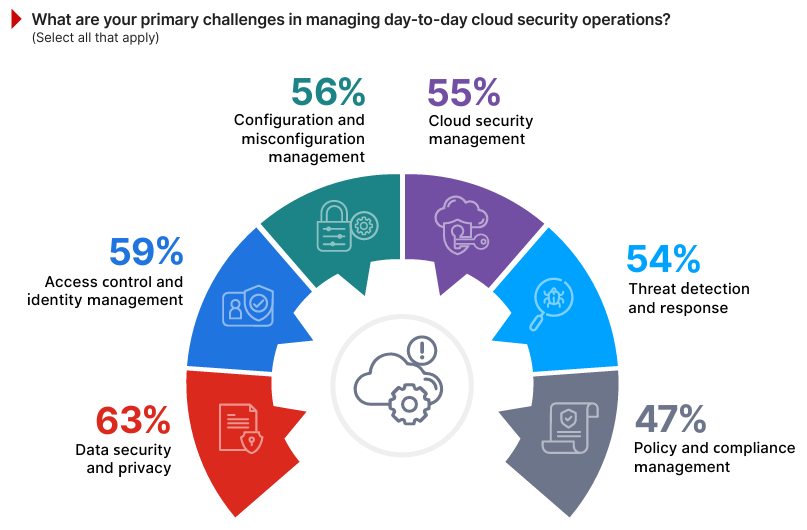
Operational Challenges in Cloud Security
Managing day-to-day cloud security operations reveals the complex and evolving hurdles organizations face in securing their environments.
Data security and privacy emerges as the top concern, identified by 63% of respondents, reflecting ongoing fears about protecting sensitive information and preventing leaks. Access control and identity management follows at 59%, underscoring the need for robust authentication and privilege management in distributed cloud environments. A hybrid cloud deployment, for instance, may face challenges in synchronizing user access policies across on-premises systems and cloud platforms.
Configuration and misconfiguration management is a close third at 56%, illustrating the operational difficulty of ensuring proper cloud setups — such as monitoring for unintentional public exposure of cloud storage buckets, a scenario that has led to numerous high-profile breaches.
Cloud security management (55%), threat detection and response (54%), and policy and compliance management (47%) collectively highlight the need for consistent and scalable solutions to manage multi-cloud environments.
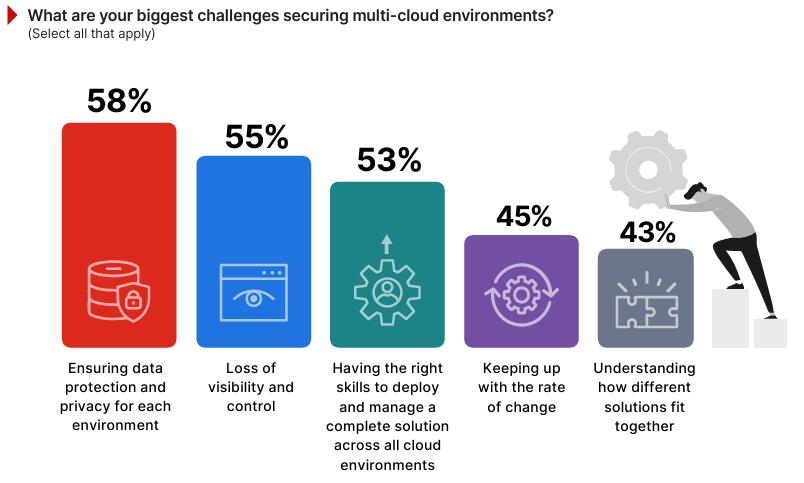
Securing Multi-Cloud Environments
Securing multi-cloud environments introduces distinct challenges stemming from their inherent complexity, lack of standardization, and rapidly evolving technologies. These issues directly impact organizations’ ability to protect sensitive data, maintain operational efficiency, and manage diverse cloud ecosystems.
Ensuring data protection and privacy for each environment continues to be the leading challenge, cited by 58% of respondents, up from 55% in 2024. This mirrors earlier findings in our survey where data security and privacy were identified as the top operational concern (63%), emphasizing the need for consistent safeguards across fragmented cloud infrastructures.
Loss of visibility and control, at 55%, underscores the difficulty of maintaining oversight in multi-cloud setups—a concern echoed previously where 55% highlighted cloud security management as a daily challenge.
The lack of skills to deploy and manage comprehensive multi-cloud solutions is cited by 53%. Challenges such as keeping up with the rate of change (45%) and understanding how different solutions fit together (43%) reflect the operational and strategic hurdles of navigating the rapid evolution of cloud technologies.
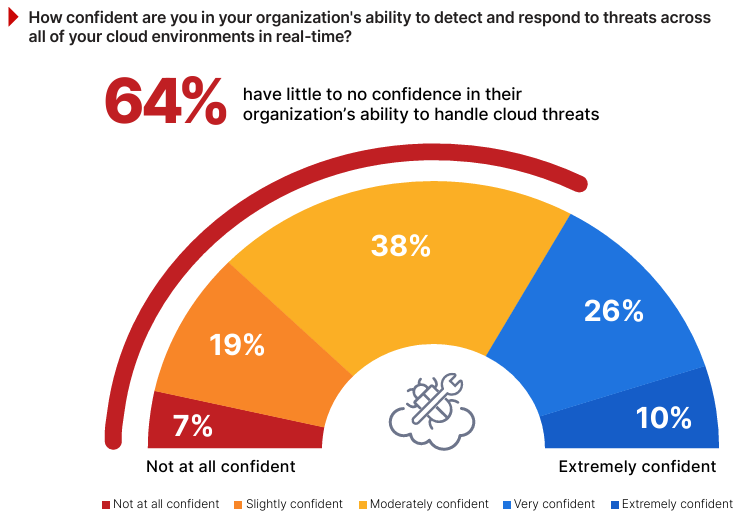
Low Confidence in Real-Time Threat Detection
The ability to detect and respond to threats across cloud environments in real time is critical as organizations adopt increasingly complex multi-cloud and hybrid strategies. These architectures introduce unique challenges in achieving seamless visibility and rapid responsiveness across disparate platforms.
The survey data highlights a significant confidence gap, with 64% of respondents indicating they lack confidence in their organization’s ability to handle real-time threat detection. For example, an organization may lack the ability to link together a series of isolated malicious actions, leading to significant delays in identifying and responding to a potential breach. This trend suggests that while many organizations have foundational security measures in place, the growing sophistication of cloud threats and the challenges of managing diverse environments leave them vulnerable to advanced attacks and misconfigurations. Survey findings discussed earlier align with this, showing that loss of visibility and control (55%) and challenges in threat detection and response (54%) are top barriers in cloud security operations.
Only 10% of respondents report being extremely confident and another 26% feel very confident, leaving fewer than 40% well-prepared for the demands of modern cloud threat management.
Cloud Security Priorities
As organizations expand their cloud footprints, deploying the right mix of security capabilities is essential to ensure resilience, compliance, and operational efficiency in the face of growing threats.
When asked about the adoption priorities for critical cloud security tools over the next 12 months, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) leads with 67%, underscoring its critical role in identifying and remediating misconfigurations across cloud environments. For example, a CSPM tool might alert a retailer of publicly exposed storage buckets in AWS, preventing a costly data breach.
Similarly, Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP), at 62%, showcase growing recognition of the need for end-to-end application lifecycle security. A CNAPP might proactively flag vulnerabilities in containerized workloads running in Kubernetes, identify malicious runtime activity, and detect a chain of events that indicate compromise. Close behind, Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP), at 60%, and Cloud Detection and Response (CDR), at 59%, highlight the increasing focus on workload security and threat mitigation, especially in multi-cloud setups. The adoption of Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM), at 50%, further demonstrates the demand for robust access and privilege controls across diverse cloud platforms and the drive towards implementing least privilege or eliminating unused credentials.

Addressing the Cybersecurity Skills Gap
The industry-wide shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals continues to be a critical issue that directly impacts an organization’s ability to protect its assets and respond effectively to evolving threats.
The findings reveal that 95% of respondents are moderately to extremely concerned about the ongoing cybersecurity skills shortage, highlighting the significant strain it places on organizations as they struggle to recruit and retain the talent needed to address increasingly complex cybersecurity challenges. For instance, a healthcare provider struggling to implement multi-cloud security controls might face delays due to the lack of specialized talent in cloud-specific skills like configuration management or CIEM.
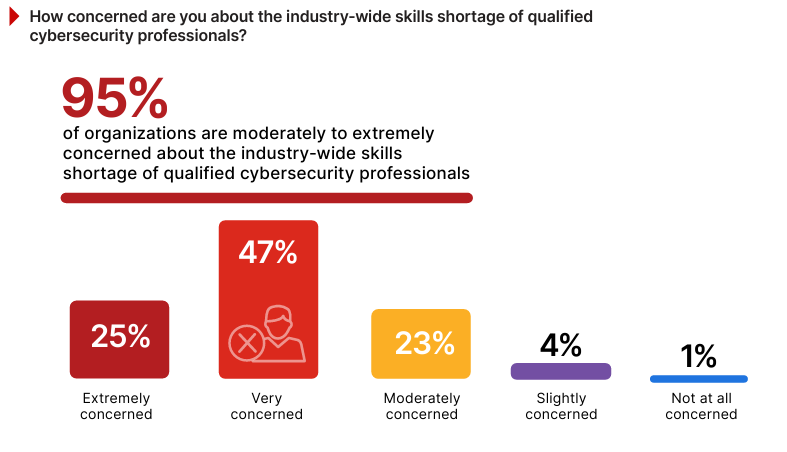
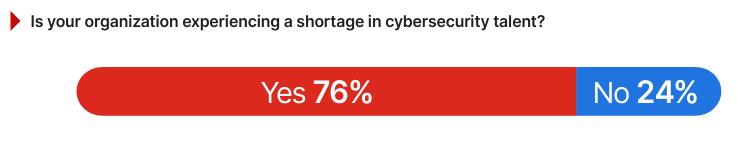
This concern is validated by survey data showing that 76% of organizations are experiencing a cybersecurity talent shortage today.
Key Security Skills for Today’s Threats
The survey findings on the most important security skills highlight the diverse and evolving expertise organizations require to tackle increasingly complex cloud security challenges.
Cloud and application security skills lead the list at 65%, reflecting the priority organizations place on securing cloud platforms and applications. For example, expertise in cloud platform-specific security might involve creating automated guardrails and scalable, secure landing zones, all available as code for automated deployment.
Identity and access management follows closely at 61%, emphasizing the need for robust access controls, particularly in hybrid and multi-cloud environments where unified user privilege management is essential. Technical and advanced security skills (58%) and threat intelligence and analysis (57%) reflect the rising demand for specialists capable of leveraging AI and understanding sophisticated adversary tactics, in order to quickly identify and mitigate malicious activity, particularly for compromised cloud admin accounts. Skills in incident response and forensics (55%) remain essential for mitigating breaches, while security monitoring and operations (52%) showcase the need for expertise in detecting anomalies and accelerating mitigation.

Investment Trends in Cloud Security
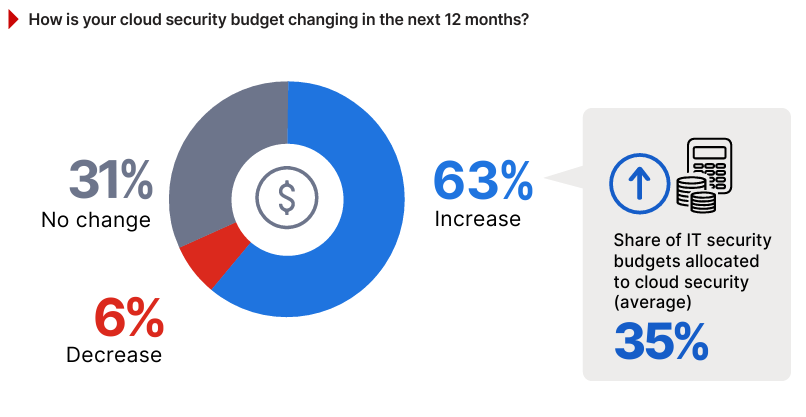
The survey results reveal fresh insights into how organizations are prioritizing their financial resources to address cloud security challenges. A majority of 63% of respondents report plans to increase their cloud security budgets in the next 12 months (up from 61% last year), signaling a strong recognition of the need to bolster defenses in hybrid and multi-cloud setups.
Meanwhile, 31% indicate unchanged budgets (down from 32% in 2024), likely reflecting organizations that have already invested heavily or are managing consistent operational needs. Only 6% expect a decrease, a rare trend in an era of escalating cloud threats and regulatory requirements.
On average, 35% of IT security budgets are allocated to security budgets, demonstrating that cloud protection is becoming a focal point of overall security spending, particularly as cloud adoption accelerates.
This growing emphasis on cloud security investment reflects a proactive approach to addressing gaps in visibility, access control, and threat detection—challenges cited throughout this report. Organizations planning budget increases should focus on solutions that efficiently integrate key capabilities, such as CNAPP, to maximize the impact of their investment.
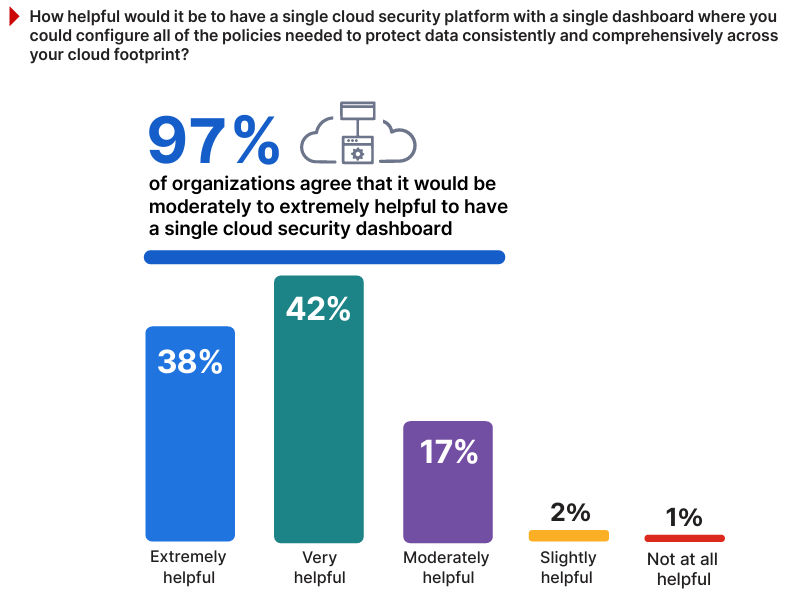
The Value of Unified Cloud Security Platforms
The value of a single, unified cloud security platform with a centralized dashboard lies in its potential to simplify policy configuration, ensure consistency, and enhance visibility across an organization’s cloud footprint.
The survey results show overwhelming interest in the concept, with 97% of respondents finding such a platform either moderately to extremely helpful. For example, a single dashboard could allow a financial services organization to apply uniform access controls across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, reducing the likelihood of configuration errors. This aligns with earlier findings where 55% of respondents cited loss of visibility and control as a primary challenge in multi-cloud and hybrid environments, emphasizing the need for centralized tools to close these gaps.
Best Practices for Stronger Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Security
As organizations increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud environments, managing diverse providers and maintaining robust security becomes more complex. To navigate these challenges effectively, it’s essential to implement strategic best practices that align with industry insights and leverage advanced security solutions.
The following recommendations offer actionable steps to enhance your multi-cloud security posture.
1.AUTOMATE DETECTION AND REMEDIATION OF CLOUD RISKS
Misconfigurations are a common vulnerability, with 67% of respondents either using or planning to adopt automated tools to address this issue. Continuous monitoring and real-time remediation solutions can proactively identify risks, such as misconfigured storage or excessive permissions, and correct them efficiently. These tools also simplify compliance with industry regulations.
2.PROTECT DATA FLOWS ACROSS CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS
As data moves between cloud environments, it is crucial to ensure its security and integrity. With 58% of respondents highlighting data protection and privacy as a top concern, leveraging tools that provide comprehensive visibility into data flows helps organizations safeguard information during transit. These tools enable monitoring for potential risks, prevent unauthorized access, and facilitate adherence to regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA, enhancing overall data protection efforts.
3.IMPLEMENT UNIFIED THREAT DETECTION MECHANISMS
Over half of respondents (54%) highlighted difficulties in detecting and responding to threats across multi-cloud environments. Unified threat detection solutions centralize visibility, allowing teams to identify and respond to anomalies quickly. These tools can correlate data across different cloud environments to reduce detection times and improve response accuracy.
4.INVEST IN CLOUD-SPECIFIC TRAINING FOR SECURITY TEAMS
Skills shortages impact 76% of organizations, limiting their ability to deploy and manage cloud-native solutions effectively. Upskilling employees in areas like DevSecOps and container security empowers teams to address emerging security challenges.
5.UTILIZE POLICY-AS-CODE FOR CONSISTENT SECURITY ENFORCEMENT
As 43% of respondents reported challenges understanding how different solutions integrate, leveraging policy-as-code approaches ensures consistent enforcement across platforms. Policyas-code simplifies audits and enables automated configuration management, ensuring that security controls remain aligned with organizational requirements.
6.ALIGN SECURITY INVESTMENTS WITH APPLICATION WORKLOAD REQUIREMENTS
Application-level security is a growing priority, with 62% of respondents planning to adopt comprehensive protection platforms. End-to-end security for applications, from development to runtime, ensures tailored protection for workloads while supporting consistent policies across environments. Solutions that integrate with containerized environments and runtime protections address this need effectively.
7.STANDARDIZE ACCESS CONTROLS ACROSS CLOUD PLATFORMS
Access control and identity management remains a top challenge for 59% of organizations, especially in distributed cloud setups. Centralized access control solutions can streamline user privilege management and enforce consistent security policies across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Implementing a unified identity platform ensures seamless policy enforcement while minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
8.EMBRACE CLOUD-BASED SECURITY TOOLS FOR SCALABILITY
With 54% of respondents identifying hybrid cloud as their primary deployment model, scalable cloud-based security tools are essential. These solutions enable consistent protection across on-premises systems and public clouds, ensuring organizations can expand their cloud footprints without compromising operational efficiency.
Conclusion
This report underscores the importance of strategic investment in unified tools, training, and processes tailored to the evolving demands of hybrid and multi-cloud security. By addressing the challenges—such as misconfigurations, skills gaps, and lack of visibility—organizations can build a resilient security posture.
Implementing the best practices provided in this report equips businesses to thrive in complex cloud environments, safeguarding critical assets while maintaining agility and compliance in an era of rapid digital transformation.
Cloud Security Glossary
This glossary provides a quick overview of essential cloud security technologies discussed in this report, focusing on what they do, the security challenges they solve, and why they matter in protecting today’s complex cloud environments.
Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) – ASPM provides visibility into application vulnerabilities and configuration issues across the software development lifecycle. It supports secure coding practices and integrates security into DevSecOps workflows. ASPM is crucial for ensuring that applications remain secure from development through deployment and runtime.
Cloud Detection and Response (CDR) – CDR is a specialized technology that identifies and mitigates threats in cloud environments. It offers real-time visibility into cloud activities, enabling quick detection of anomalies and swift incident response. CDR is crucial for maintaining a strong defense against sophisticated threats in distributed cloud setups.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) – CIEM focuses on managing permissions and access controls within cloud environments. It identifies excessive permissions, enforces least-privilege principles, and reduces the risk of privilege misuse. CIEM is important for maintaining secure and compliant access policies in multi-cloud architectures.
Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) – CNAPP integrates multiple security functions to protect cloud-native applications throughout their lifecycle. It combines workload protection, configuration management, and runtime defense to secure containers, serverless functions, and other cloud-native workloads. CNAPP is essential for organizations adopting modern development practices like DevOps and microservices.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) – CSPM is a solution designed to automate the detection of misconfigurations in cloud environments. It continuously monitors cloud infrastructure for security risks, such as exposed storage buckets or overly permissive access controls, ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. CSPM is critical for maintaining visibility and addressing vulnerabilities in multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) – CWPP secures workloads across cloud environments, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless architectures. It provides visibility into vulnerabilities, ensures consistent security policies, and protects workloads from advanced threats. CWPP is key for organizations managing diverse and dynamic cloud workloads.
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) – DSPM is a data-centric solution that identifies, classifies, and secures sensitive information in cloud environments. It ensures that data is properly protected and aligns with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. DSPM is vital for addressing the challenges of safeguarding sensitive information across complex cloud ecosystems.
Methodology and Demographics
The 2025 Cloud Security Report is based on a comprehensive survey conducted in late 2024, gathering insights from 873 IT and cybersecurity professionals across a range of countries and industries, including technology, financial services, healthcare, and government. Respondents represented organizations of varying sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises, and included professionals in roles ranging from specialists to C-level executives.
The survey, conducted online, explored key trends, challenges, and priorities in cloud security. The findings provide a well-rounded view of how organizations are navigating the complexities of cloud environments and adopting security technologies to address emerging threats.
For questions that allow respondents to select multiple answers, the percentages may total more than 100%, as participants could choose more than one option.
__
Fortinet (NASDAQ: FTNT) secures the largest enterprises, services providers, and government organizations around the world. Fortinet empowers our customers with complete visibility and control across the expanding attack surface and the power to take on ever-increasing performance requirements today and into the future. Only the Fortinet Security Fabric platform can address the most critical security challenges and protect data across the entire digital infrastructure, whether in networks, application, multi-cloud, or edge environments. Fortinet ranks #1 as a security company, with more than 800,000 clients who trust their solutions and services to protect their businesses. www.fortinet.com
__
Cybersecurity Insiders brings together 600,000+ IT security professionals and world-class technology vendors to facilitate smart problem-solving and collaboration in tackling today’s most critical cybersecurity challenges. Our approach focuses on creating and curating unique content that educates and informs cybersecurity professionals about the latest cybersecurity trends, solutions, and best practices. From comprehensive research studies and unbiased product reviews to practical e-guides, engaging webinars, and educational articles – we are committed to providing resources that provide evidence-based answers to today’s complex cybersecurity challenges. Contact us today to learn how Cybersecurity Insiders can help you stand out in a crowded market and boost demand, brand visibility, and thought leadership presence. Email us at info@cybersecurity-insiders.com or visit cybersecurity-insiders.com
The post State of Cloud Security Report 2025 first appeared on Cybersecurity Insiders.
The post State of Cloud Security Report 2025 appeared first on Cybersecurity Insiders.
March 28, 2025 at 02:05PM











